- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
дек. . 18, 2024 00:44 Back to list
The Evolution of Industrial Buildings A Testament to Innovation and Functionality
Industrial buildings have been essential to the development of modern society, serving as the backbone of manufacturing, production, and innovation. These structures have undergone significant transformations over the years, reflecting advancements in technology, changes in economic conditions, and evolving design philosophies.
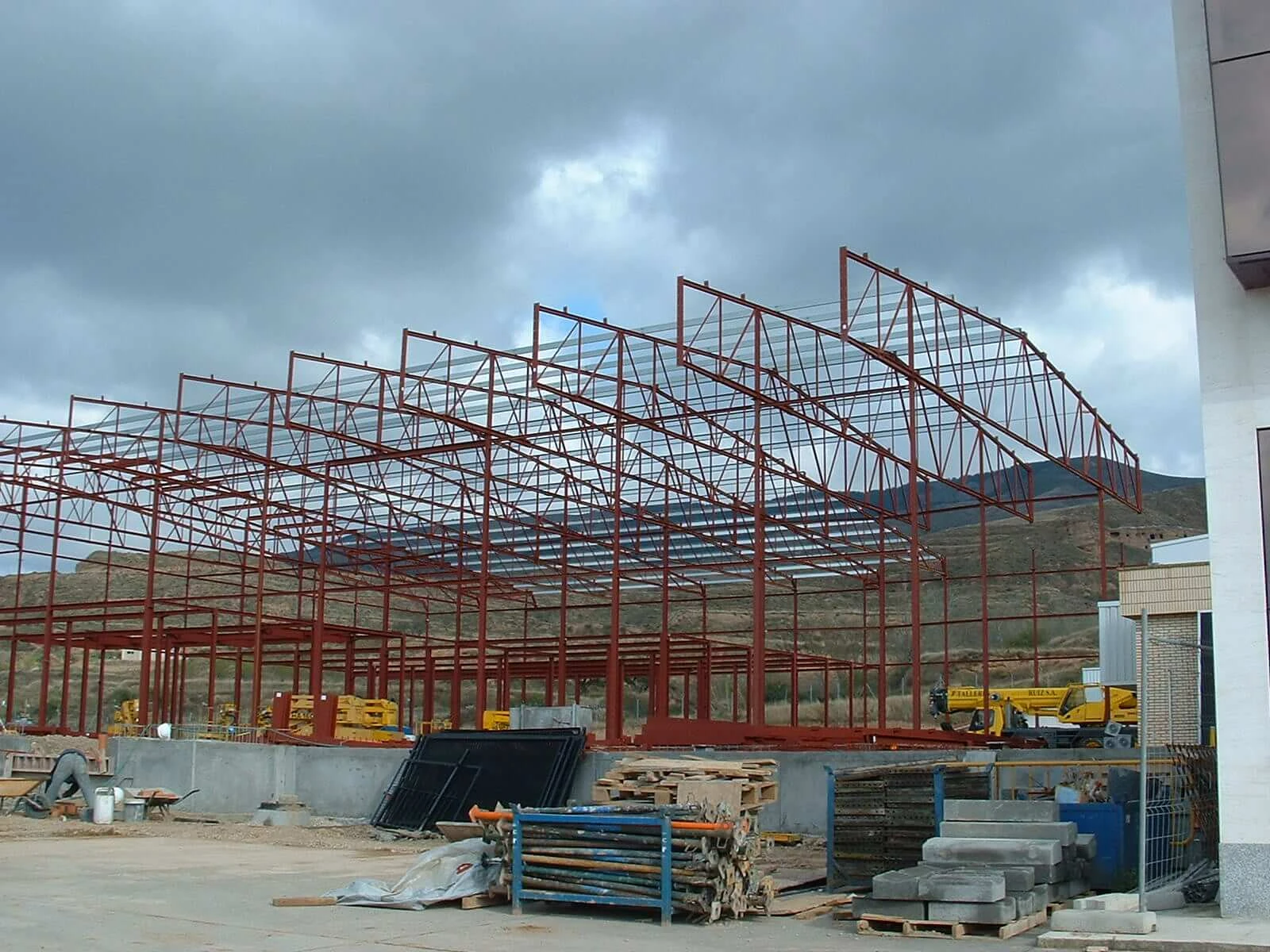
The origin of industrial buildings can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. This era marked a dramatic shift from agrarian economies to industrial powerhouses. Factories began to emerge as centers of productivity, where machinery replaced manual labor in producing goods on a much larger scale. These early industrial buildings were often utilitarian, constructed from robust materials like brick and stone to withstand the rigors of heavy machinery and large-scale operations.
As industries expanded, the architectural style of industrial buildings began to reflect the needs of more complex processes. The introduction of iron and steel into construction allowed for larger spans and more open floor plans, leading to the designing of factories that could accommodate increasingly sophisticated machinery and workflows. The Crystal Palace in London, built in 1851, is a prominent early example of this evolution, showcasing the potential of glass and iron in industrial architecture. It symbolized not only the capabilities of industrial technology but also the aesthetic possibilities of industrial design.
The early 20th century saw another wave of transformation in industrial buildings, driven by innovations such as reinforced concrete. This material provided greater flexibility in design, allowing for taller structures and more intricate layouts. The design philosophies of the time began to embrace functionality while also considering the worker’s experience. Factories were now designed with large windows for natural light, open spaces to facilitate movement, and consideration for worker safety and comfort.
industrial building

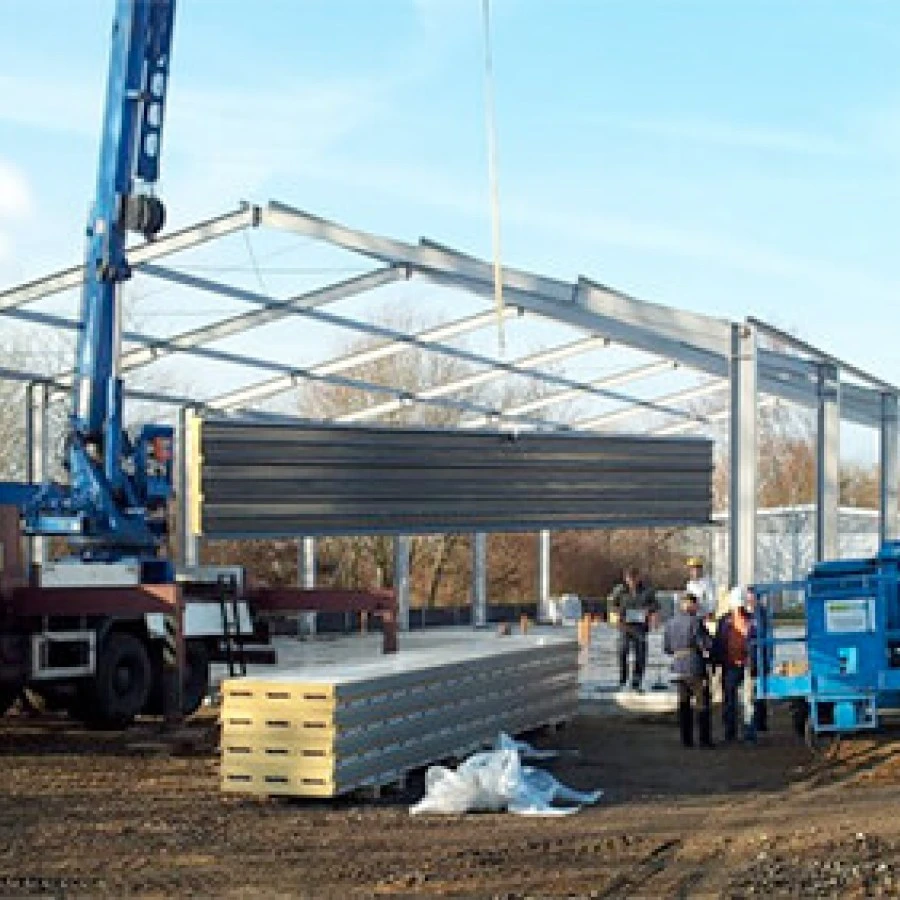
With the post-World War II economic boom, industrial buildings diversified further. The growth of consumer culture led to a rise in manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and distribution centers. The architectural approach became more standardized, with many buildings adopting a modular design that allowed for quicker construction and adaptability to various industrial needs. These structures often featured extensive loading docks and clear span interiors to accommodate the logistics and transportation that were becoming vital components of the supply chain.
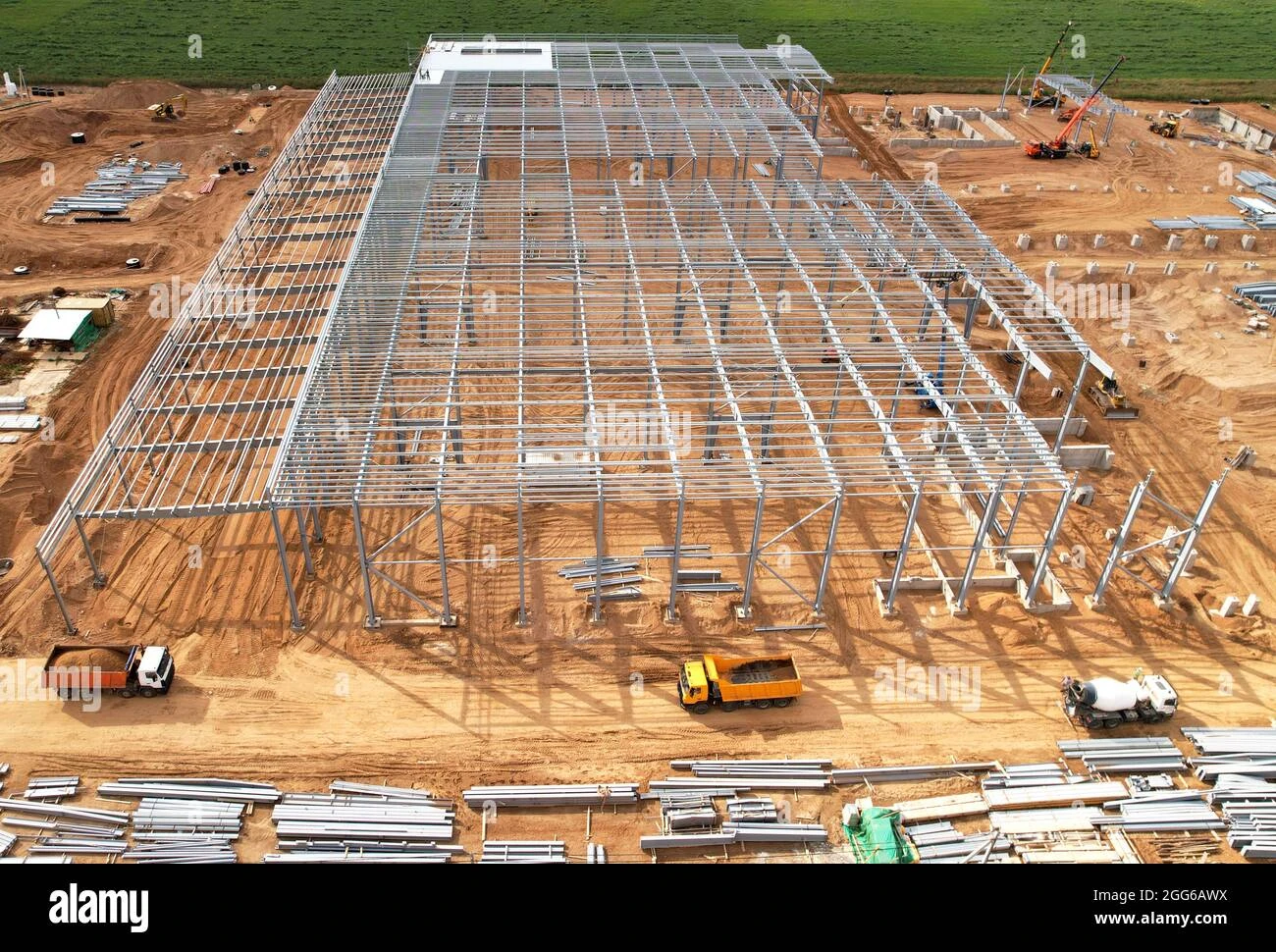
In recent decades, the advent of the digital age has influenced the design and function of industrial buildings once again. Advanced technologies such as automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence are reshaping the way goods are produced and distributed. Smart factories are emerging, integrating IoT (Internet of Things) systems that allow for real-time monitoring and optimization of production processes. Industrial buildings are being designed with these technologies in mind, incorporating advanced energy-efficient systems, flexible workspaces, and innovative materials that enhance functionality and reduce environmental impact.
Sustainability has become a critical focus for modern industrial buildings. As awareness of climate change and environmental issues grows, new constructions emphasize green building practices. This includes using renewable energy sources, sustainable materials, and designs that minimize ecological footprints. The adaptive reuse of older industrial structures has also gained traction, honoring the historical significance of these buildings while repurposing them for contemporary needs. For instance, disused factories are transformed into lofts, office spaces, or community hubs, preserving cultural heritage while meeting current demands.
In conclusion, industrial buildings have evolved significantly over the past two centuries, from simple, utilitarian structures to complex environments that foster innovation and efficiency. They remain a critical element of our economy and continue to adapt to technological advancements and societal needs. As we look to the future, these buildings will undoubtedly undergo further transformations, reflecting our ongoing quest for sustainability, efficiency, and resilience in an ever-changing world. As such, they will not only house the means of production but will also symbolize the creative spirit and ingenuity of human endeavor.
-
Cold Formed Steel Residential Framing
NewsMay.21,2025
-
Innovative Steel Structure Building Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
-
Innovative Prefab Metal Shed Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
-
Durable Steel Horse Shelter Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
-
Durable Metal Shed Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
-
Durable Big Metal Shed Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.