- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Apr . 27, 2025 22:30 Back to list
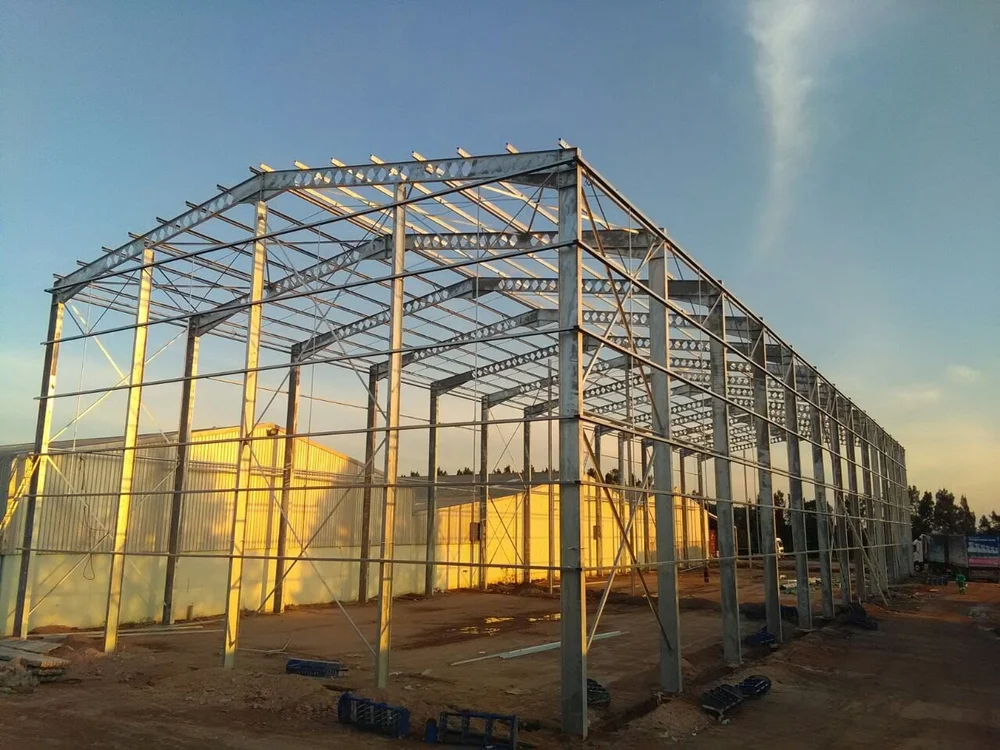
- Overview of Prefabricated Engineered Buildings
- Technical Advantages and Material Innovation
- Leading Manufacturers: A Comparative Analysis
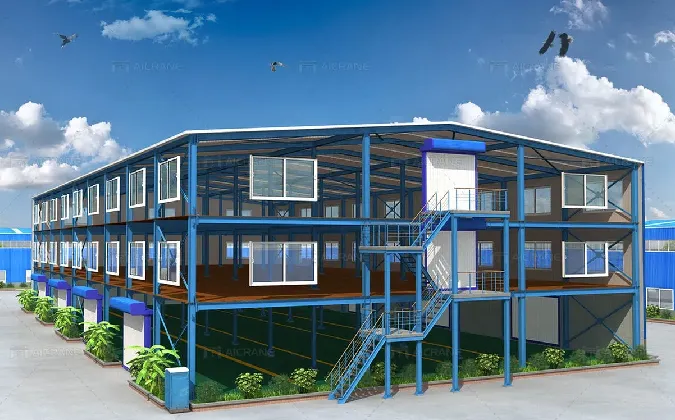
- Customization Solutions for Diverse Needs
- Case Studies: Real-World Applications
- Sustainability and Cost Efficiency
- Future Trends in Pre Engineered Building Design
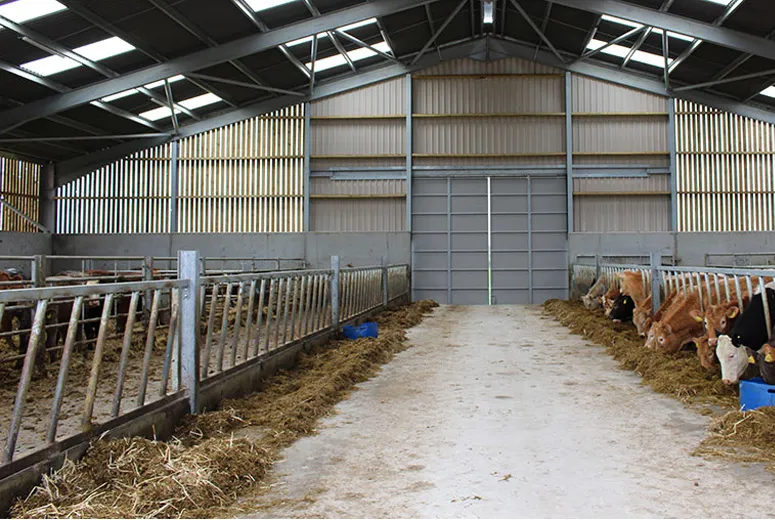

(prefabricated engineered building)
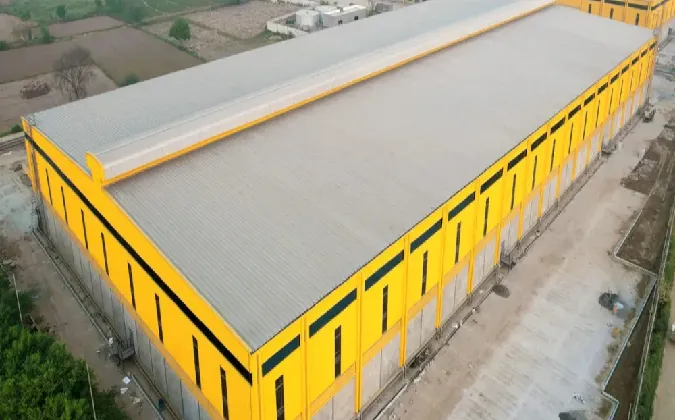
Prefabricated Engineered Buildings: Revolutionizing Construction
The global prefabricated engineered building
market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030, driven by demand for rapid, scalable construction. These structures utilize advanced engineering principles to reduce material waste by up to 30% compared to traditional methods. By integrating BIM (Building Information Modeling) and lean manufacturing, manufacturers deliver projects 40-50% faster than conventional approaches.
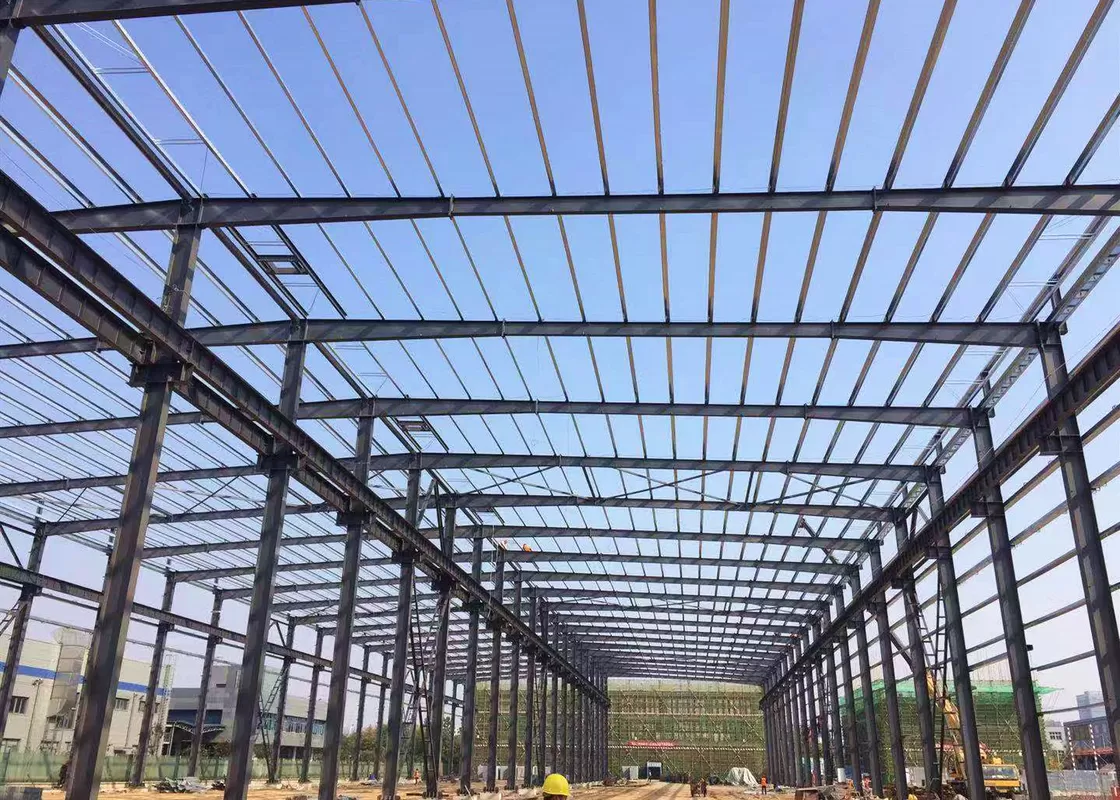
Technical Superiority in Modern Construction
Advanced steel alloys and composite panels enable spans up to 90 meters without intermediate supports. Key innovations include:
- High-strength galvanized steel (G550-Z275 coating)
- Automated roll-forming machines (±0.5mm precision)
- Thermal-efficient insulation (U-values as low as 0.25 W/m²K)
Structural simulations show 25% better load distribution compared to conventional designs, with seismic resistance exceeding IBC 2021 standards by 15%.
Manufacturer Comparison: Key Industry Players
| Manufacturer | Experience | Projects Completed | Lead Time | Customization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | 35+ years | 12,500+ | 8-10 weeks | Full modular |
| Company B | 28 years | 9,200+ | 6-8 weeks | Semi-custom |
| Company C | 42 years | 18,000+ | 10-12 weeks | Full bespoke |
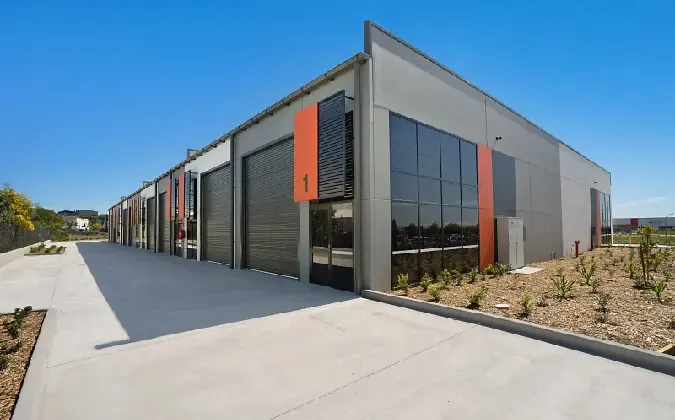
Tailored Solutions for Specific Requirements
Customization options address diverse operational needs:
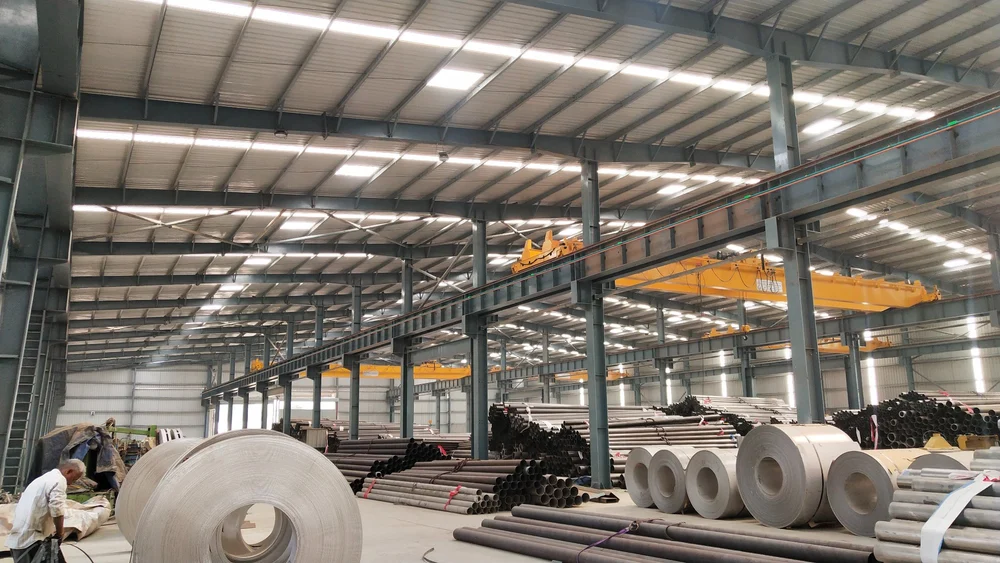
- Warehousing: Clear heights up to 40m with 150kN/m² floor loading
- Commercial: Architectural finishes with 60dB acoustic rating
- Industrial: Chemical-resistant coatings (ASTM B117 compliant)
Case Example: A 15,000m² distribution center achieved 22% cost reduction through optimized column spacing and hybrid foundation systems.
Demonstrated Success Across Industries
Notable implementations include:
- 78,000m² automotive plant in Germany (completed in 19 weeks)
- 35-story hybrid structure in Singapore (85% prefabricated components)
- Cold storage facility in India maintaining -30°C with 45% energy savings
Eco-Friendly Construction Methodology
Lifecycle analysis reveals 38% lower embodied carbon versus traditional builds. Energy modeling shows 25-30% reduction in operational costs through:
- Integrated solar-ready roofing systems
- Smart ventilation with 92% heat recovery
- Recyclable steel content exceeding 96%
Innovations in Pre Engineered Building Design
Emerging technologies like AI-driven structural optimization are reducing material requirements by an additional 12-18%. Digital twin integration enables real-time performance monitoring, with leading manufacturers reporting 99.2% design accuracy. The sector is moving toward fully automated plants capable of producing 50 tonnes of fabricated steel daily with 0.3% error margins.

(prefabricated engineered building)
FAQS on prefabricated engineered building
Q: What is a prefabricated engineered building?
A: A prefabricated engineered building is a structure designed and manufactured off-site using standardized components. These buildings are optimized for quick assembly, cost-efficiency, and structural durability, often used for warehouses, factories, and commercial spaces.
Q: How does pre-engineered building design improve construction timelines?
A: Pre-engineered building design utilizes computer-aided modeling to streamline component fabrication and reduce on-site labor. This approach minimizes design errors and ensures faster project completion compared to traditional construction methods.
Q: What should I look for in pre-engineered building manufacturers?
A: Choose manufacturers with certifications like ISO or AISC, proven experience in your industry, and customization capabilities. Ensure they offer end-to-end services, including design support, material quality guarantees, and post-installation maintenance.
Q: Can prefabricated engineered buildings be customized for specific needs?
A: Yes, modern pre-engineered buildings allow customization in dimensions, cladding materials, and interior layouts. Manufacturers adapt designs to meet functional requirements like insulation, ventilation, or seismic resistance.
Q: Are pre-engineered buildings environmentally sustainable?
A: Many pre-engineered buildings use recyclable steel and minimize waste through precise fabrication. Their energy-efficient designs, including options for solar panels or insulated panels, also reduce long-term environmental impact.
-
The Strength and Versatility of Industrial Metal Infrastructure
NewsAug.05,2025
-
The Landscape of Industrial Fabrication: Steel and Metal Factory Infrastructure
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Innovative Solutions for Industrial and Storage Spaces: Metal Building Garages and Workshops
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Evaluating Expenditures for Prefabricated Warehouse Structures
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Diverse Solutions for Industrial Spaces: Metal Workshop Buildings
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Analyzing Costs and Solutions in Industrial Steel Construction
NewsAug.05,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.