- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
नोभ . 09, 2024 22:56 Back to list
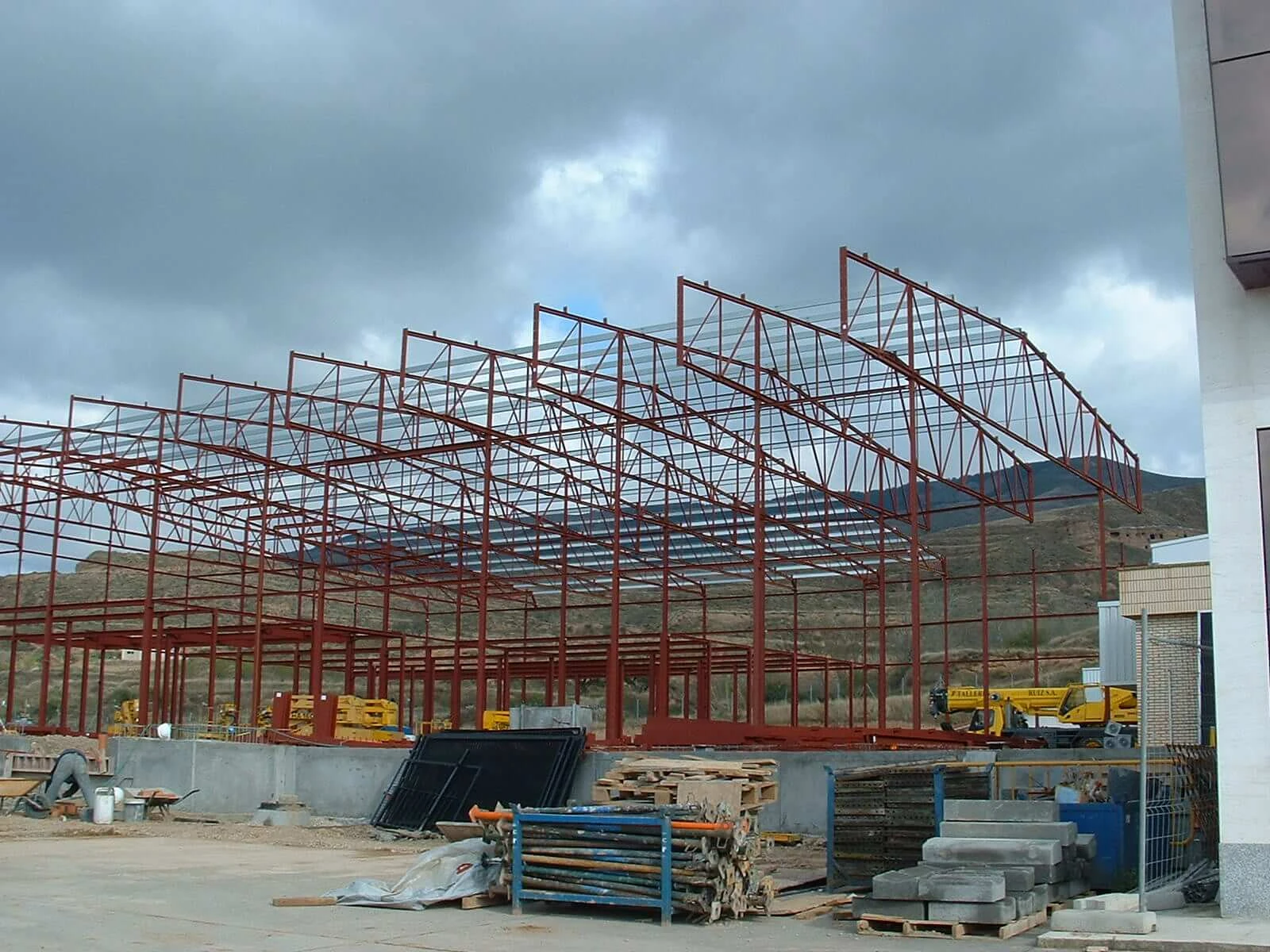
Foundation Footing Design for Steel Buildings An Overview
Designing a foundation for a steel building is a critical aspect of ensuring its stability and longevity. The footing serves as the bottom support of the structure, distributing the loads from the building to the ground below. Proper footing design is essential to prevent settling, tilting, or other structural failures. In this article, we will explore the key considerations and steps involved in designing foundations and footings for steel buildings.
Understanding Load Types
The design process begins with a thorough understanding of the loads the building will experience. These loads can be classified into several types dead loads (the weight of the building materials), live loads (occupants, furniture, and movable equipment), wind loads, seismic loads, and snow loads, among others. Each of these loads needs to be accurately calculated and considered in the footing design to ensure that the foundation can safely support the building.
Soil Analysis
Before any design work can begin, a detailed soil analysis is required. This analysis usually involves geotechnical investigations, including soil boring tests, to determine the soil’s properties, such as its bearing capacity, density, moisture content, and compaction characteristics. Understanding the soil’s behavior under load is crucial, as different soil types will influence the depth and size of the footings. Soil bearing capacity directly impacts how much load a foundation can support and helps determine the appropriate footing design.
Footing Types and Design
There are various types of footings used in steel building foundations, including spread footings, continuous footings, pile foundations, and mat foundations. The choice of footing type depends on several factors, including load requirements, soil conditions, and building design.
1. Spread Footings These are commonly used and consist of a concrete slab that spreads the load over a larger area. They are typically placed beneath columns and walls and are suitable for stable soil conditions.
foundation footing design for steel buildings

3. Pile Foundations When soil bearing capacity is low, pile foundations can transfer loads to deeper, more stable soil layers or bedrock. Piles can be concrete, steel, or timber.
4. Mat Foundations Used for heavy structures or poor soil conditions, mat foundations consist of a thick concrete slab that supports the entire structure, helping to spread the load evenly.
The design of these footings must comply with relevant building codes and standards, taking into account factors such as frost depth, load factors, and material properties.
Reinforcement Considerations
To ensure that footings can withstand the various stresses they may encounter, proper reinforcement is crucial. Steel reinforcement bars (rebar) are commonly integrated into the concrete mix to enhance tensile strength. The layout, size, and spacing of the rebar must be carefully calculated based on the anticipated loads and structural requirements.
Settling and Differential Movement
Designing footings also requires consideration of settling and differential movement. Differential settling can cause structural damage, particularly in steel buildings. Engineers must account for potential uneven settling of the foundation due to soil compaction over time or variations in soil characteristics. Techniques such as using flexible connections between structural elements can help mitigate the effects of movement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, foundation footing design for steel buildings is a complex but essential process that involves careful consideration of various factors, including load analysis, soil conditions, footing types, reinforcement strategies, and potential settling issues. A well-designed foundation is the key to a stable and durable building, supporting its structure through various environmental conditions and ensuring its longevity. Engaging experienced professionals in geotechnical engineering and structural design is crucial to achieving optimal results in foundation design.
-
Cold Formed Steel Residential Framing
NewsMay.21,2025
-
Innovative Steel Structure Building Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
-
Innovative Prefab Metal Shed Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
-
Durable Steel Horse Shelter Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
-
Durable Metal Shed Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
-
Durable Big Metal Shed Solutions
NewsMay.19,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.