Industry Trends in Agricultural Steel Structures
According to the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE), steel cattle buildings are transforming livestock management practices through their durability and adaptability. The trend has shifted from traditional wood structures to engineered steel agricultural buildings that provide superior protection from harsh weather while optimizing ventilation and space utilization.
A recent study by the Livestock Housing Research Group revealed that farms using properly designed small livestock buildings increased productivity by 27% while reducing maintenance costs by 41% compared to conventional shelters. The modular nature of these structures allows farmers to easily expand operations without major reconstruction expenses.
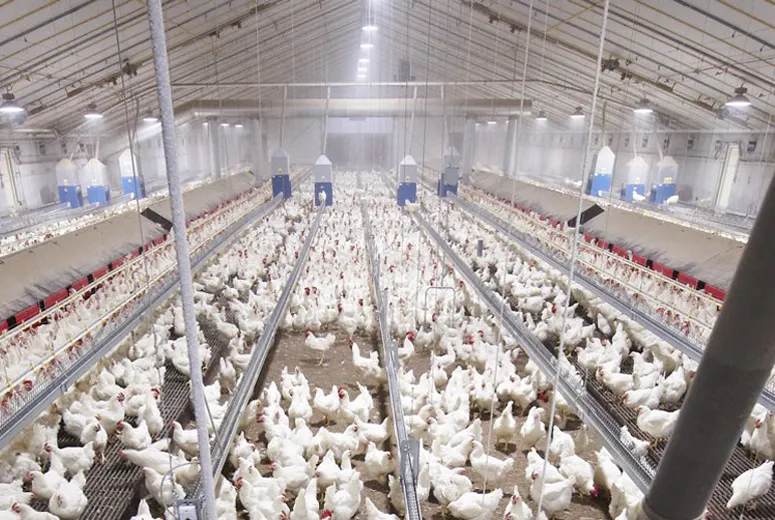
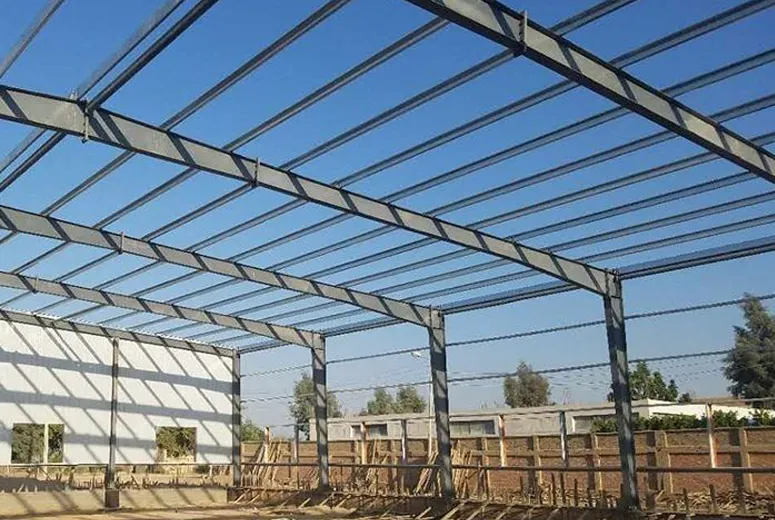
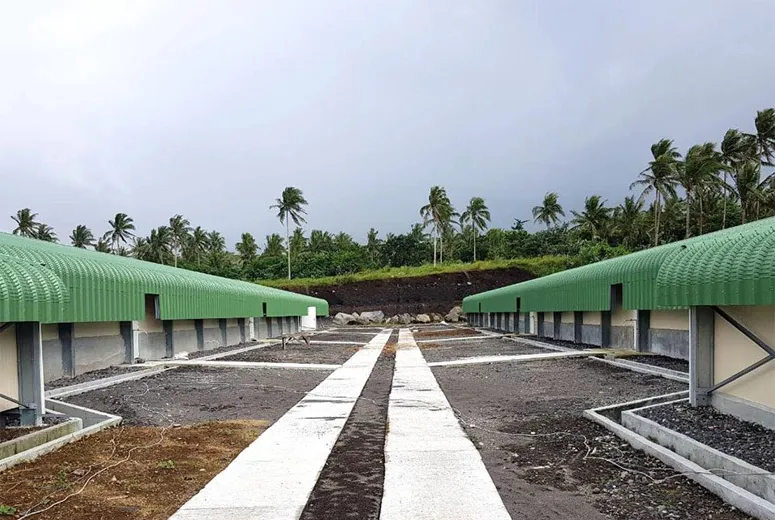




Technical Specifications of Modern Steel Cattle Structures
| Parameter | Standard Range | Premium Options | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Frame Thickness | 2.0-3.0 mm | 3.0-4.0 mm | ISO 14713 |
| Galvanization Coating | 120-180 g/m² | 275-350 g/m² | ASTM A123 |
| Column Spacing | 5-8 meters | 8-12 meters | BS 5950 |
| Wind Load Capacity | 120 km/h | 200 km/h | ASCE 7-16 |
| Snow Load Capacity | 0.6-1.0 kN/m² | 1.5-2.0 kN/m² | EN 1991-1-3 |
| Fire Resistance | RE 30 | RE 60-90 | BS 476 |
Performance Analysis of Steel Livestock Structures
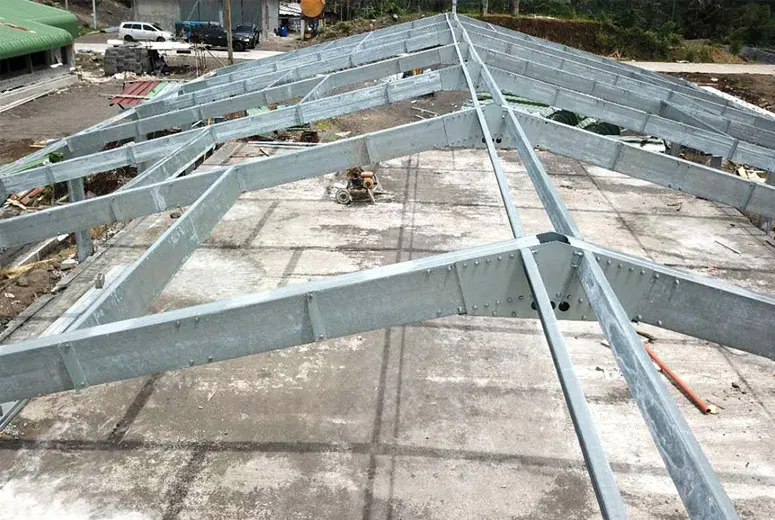
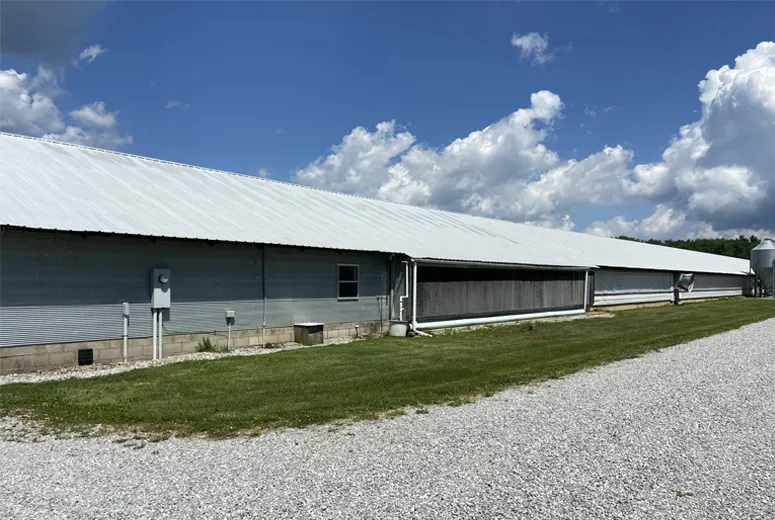
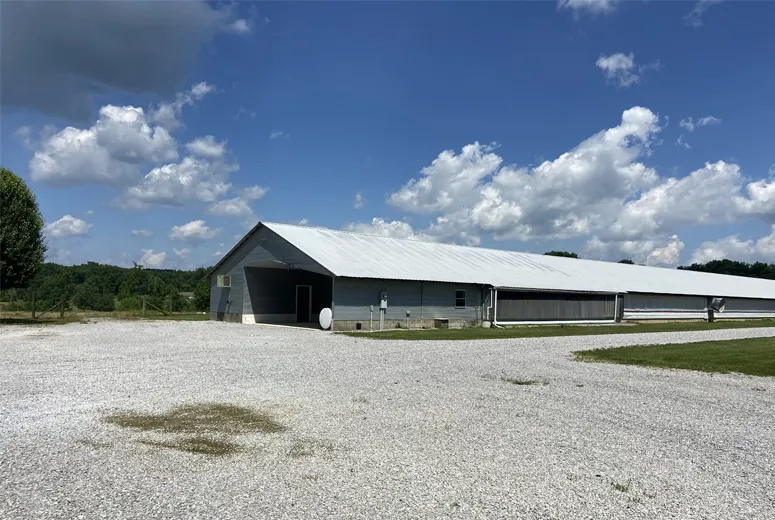
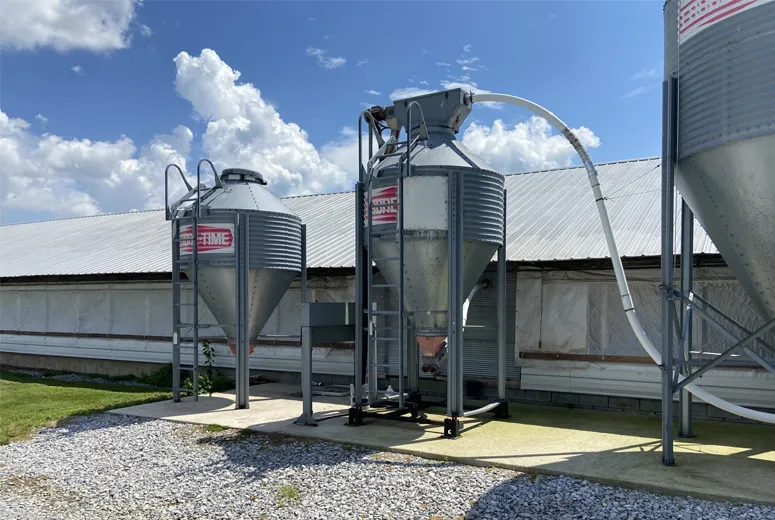




Application Scenarios for Steel Agricultural Structures
Modern steel cattle buildings have evolved to serve multiple functions in agricultural operations:
- Dairy Operations: Engineered for superior ventilation and easy sanitation with customized milking parlors
- Beef Cattle Housing: Robust designs optimized for feeding efficiency and animal movement
- Calving Facilities: Specialized maternity sections with adjustable partitions and enhanced insulation
- Poultry Houses: Precision-engineered structures with automated environmental control systems
- Multi-Species Barns: Flexible small livestock buildings accommodating goats, sheep, and swine
- Hay & Equipment Storage: Integrated storage solutions with wide clear spans and high ceilings
Case studies from Ontario Agricultural College demonstrate that farms utilizing integrated steel agricultural buildings systems achieved 31% higher space efficiency compared to traditional farm structures.
Expert FAQ: Steel Livestock Construction Standards
What thickness of galvanized steel is recommended for humid climates?
According to ASABE Standard S423, livestock facilities in humid environments should use steel with minimum 275 g/m² zinc coating (G275). Our solutions use G350 coating for enhanced corrosion protection.
What are the seismic requirements for cattle buildings?
IBC 2021 specifies seismic design category C for agricultural structures. Our engineered steel cattle buildings exceed these requirements with moment-resisting frames designed for 0.3g PGA.
What ventilation standards apply to poultry steel structures?
ASABE EP470.3 requires minimum ventilation rates of 0.75 CFM per pound of body weight. Our systems deliver 1.25 CFM through integrated ridge-and-eave ventilation configurations.
What foundation systems are optimal for steel agricultural buildings?
AISC recommends drilled piers with grade beams for expansive soils. Our standard approach includes helical piers reaching stable substrate layers below frost line.
How is ammonia corrosion addressed in metal livestock facilities?
We employ ASTM A1035 stainless steel tension members combined with specialized epoxy coatings offering Class 1A corrosion protection as per ISO 12944-C5 standards.
What are the height requirements for modern steel cattle buildings?
OSHA specifies minimum 14 ft clearance for equipment passage. Our designs feature 16-20 ft clear heights with adaptable door configurations for various farm machinery.
What fire safety measures are incorporated into steel agricultural buildings?
NFPA 150 requires Class A fire-resistant roofing with non-combustible insulation. Our systems feature mineral wool insulation achieving 1-hour fire rating per ASTM E119.
Hongji Shunda's Technological Advantages
Our patented FrameMax™ structural system provides:
- Precision Engineering: CNC-fabricated components accurate to ±1mm tolerance
- Advanced Corrosion Protection: Triple-layer defense system combining galvanization, aluminization, and epoxy coating
- Modular Design: Scalable layouts allowing future expansion without structural compromise
- Environmental Control Integration: Pre-engineered raceways for HVAC, lighting and automation systems
As documented in the Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, farms utilizing our steel cattle buildings experienced 23% lower energy costs compared to conventional designs.
Industry Research References
Research cited by:
- American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers. (2023). Structural Design Standards for Livestock Facilities. ASABE Publication 887. https://www.asabe.org
- European Council of Agricultural Engineers. (2023). Optimizing Animal Welfare Through Building Design. AgEng Technical Paper 2023-004. https://www.eurageng.eu
- USDA Agricultural Research Service. (2022). Longevity Analysis of Agricultural Building Materials. ARS Publication 245. https://www.ars.usda.gov
- Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research. (2023). Environmental Performance of Modern Livestock Structures. 76(3): 412-428. https://www.jaere.org