Oct . 28, 2025 15:35 Back to list
What’s Changing in Steel Hangar Buildings Right Now
I’ve been walking job sites for more than a decade, and the hangar conversations have shifted. General aviation is back, drones are scaling, and MRO teams want fast, clean, code-compliant space. In practice, Steel Hangar Buildings are winning because they go up quickly, handle long spans without drama, and—if engineered well—ride out tough climates without constant maintenance.
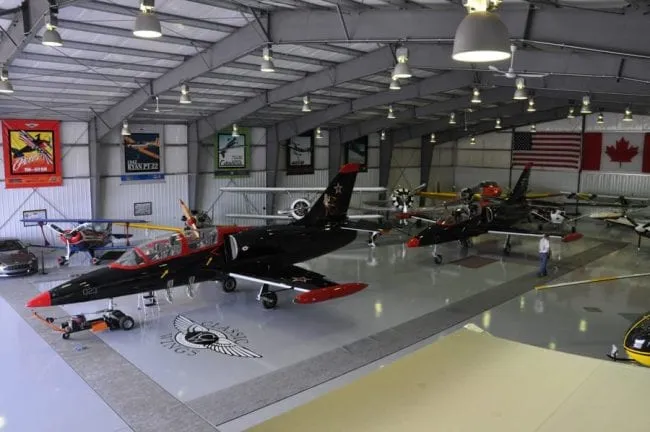

Product snapshot: Airplane Hangar Metal Buildings
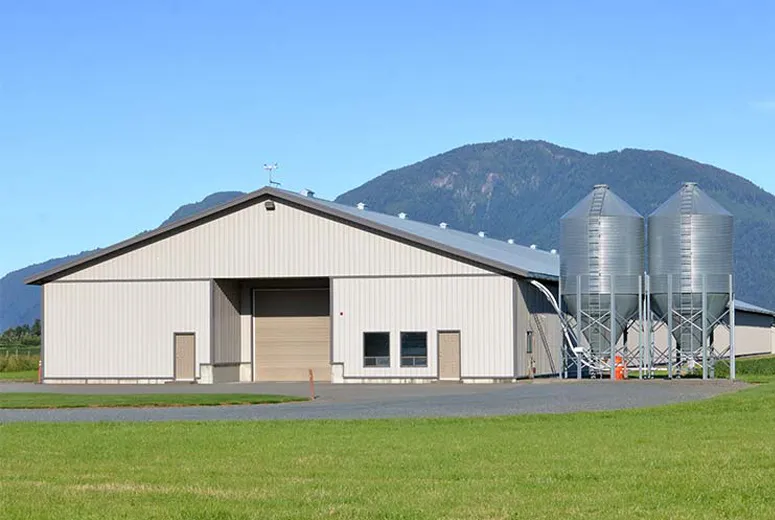
Origin: No. 1 YuLong Road, JinZhou, Shijiazhuang, Hebei. The common requests I hear line up with their popular footprints: 20×30 m, 20×50 m, 16×36 m; heights around 4–6 m; and big gates (14–18 m wide, up to 5 m tall). Cladding is typically single corrugated steel, or insulated roof with single-sheet walls—budget-friendly, upgradeable later.
| Frame steel | Q235B/Q355B (≈ ASTM A36/A572 Gr.50) |
| Spans & heights | 16–50 m span typical; 4–6 m eave height (customizable) |
| Cladding options | Single corrugated sheet; insulated roof; insulated wall panels optional |
| Door systems | Sliding, vertical-lift fabric, hydraulic (gate sizes ≈ 14–18 m × 3.5–5 m) |
| Design criteria | IBC/GB codes; AISC 360; wind ≈ 0.5–0.8 kPa; snow ≈ 0.75–1.5 kPa (real-world use may vary) |
| Corrosion protection | HDG per ISO 1461 or paint systems to ISO 12944 C3–C5 |
Where these hangars get used
- General aviation and charter (single to twin turboprops)
- MRO bays needing open floor plates and clean lighting
- Helicopter EMS and offshore shuttle ops
- UAV/drones, flight schools, and yes—car collections, too
To be honest, many customers say the biggest surprise is how quiet a well-insulated roof is during rain. Seems small—until it isn’t.
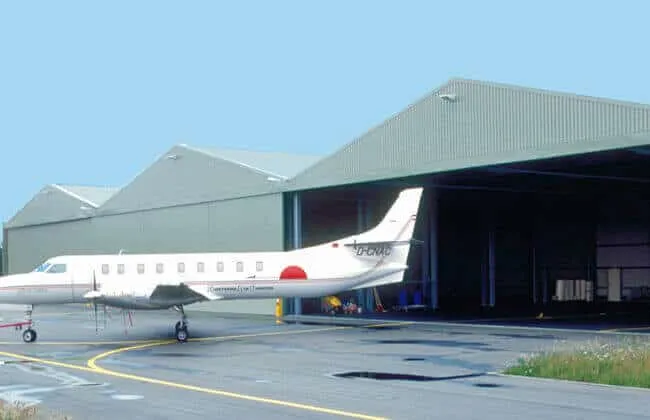

Build process, testing, and service life
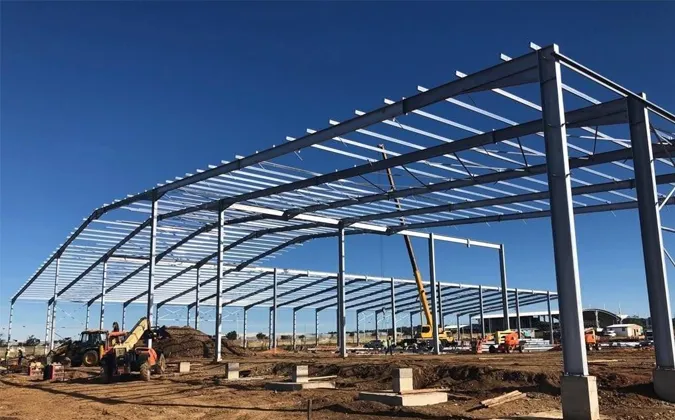
- Materials: Q235B/Q355B frames, 8.8/10.9 bolts, roof/wall sheets with optional PIR/Rockwool insulation.
- Fabrication: CNC cutting, submerged arc welding (AWS D1.1), camber control, trial fit.
- Protection: HDG or primer + intermediate + topcoat to ISO 12944 (C3–C5 depending on site).
- Testing: Weld VT/PT/UT (ISO 17638/17640), bolt torque logs, coating DFT gauges.
- Assembly: Pre-drilled kits, labeled members, on-site bolting; doors commissioned last.
- Service life: ≈ 25–50 years with correct coating class and maintenance interval.
Real-world case notes
Case A: Coastal GA base — 20×50 m, 6 m height, vertical-lift fabric door 18×5 m. C5 coating, stainless fasteners at eaves. After 18 months, inspectors noted 0 coating failures; energy use down 17% vs. older sheet-only hangar (meter data, owner-supplied).
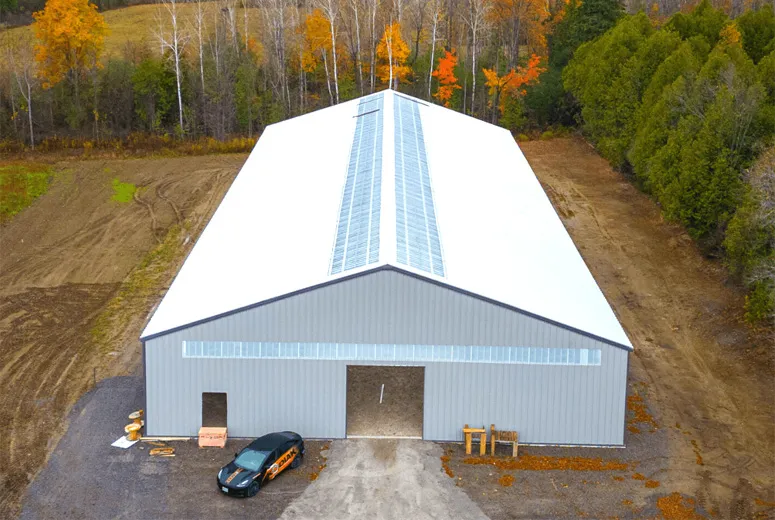
Case B: Inland flight school — 16×36 m, 5 m height, sliding doors 14×3.5 m, simple single-sheet roof. Budget-first, later upgraded to insulated roof in a weekend shutdown. “Quieter and cooler,” the manager told me.

Why Steel Hangar Buildings keep winning
- Speed: shop-fabricated, bolt-up frames reduce on-site time.
- Span-friendly: clear spans for aircraft movement and MRO cranes.
- Predictable cost: fewer surprises than bespoke concrete or timber.
- Compliance-ready: designed to IBC/AISC and NFPA 409 for hangar types.
Vendor comparison (quick read)
| Vendor | Strengths | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Hongjishunda (Airplane Hangar Metal Buildings) | Factory-direct spans; C3–C5 coatings; door options; fast lead times | Import logistics planning; verify local code official preferences |
| Local steel builder | On-site support; local permitting familiarity | Cost variability; schedule tied to regional labor availability |
| Prefab kit reseller | Lowest upfront price | Limited customization; door integration can be tricky |
Customization checklist
- Door type/clearance: sliding vs. hydraulic vs. fabric lift
- Thermal: R-values, skylights, condensation control
- Fire/life-safety: per NFPA 409 hangar group, foam/sprinklers where required
- Loads: local wind/snow, seismic category, deflection limits (L/240–L/300)
- Electrical/MEP: LED high-bays, busways, compressed air lines
Certifications and documentation available on request: ISO 9001 fabrication, material mill certs, weld maps, coating DFT logs, and anchor bolt plans. Honestly, the paperwork saves headaches at inspection.
Citations
- NFPA 409: Standard on Aircraft Hangars.
- International Building Code (IBC), latest edition.
- AISC 360: Specification for Structural Steel Buildings.
- ASTM A36/A572: Structural steel specifications.
- ISO 12944: Paint systems for corrosion protection.
- ISO 1461: Hot-dip galvanized coatings; AWS D1.1 Structural Welding Code—Steel.
-
Bolted Connections in Steel Frame Warehouse
NewsNov.17,2025
-
Hay Storage in Farm Metal Buildings
NewsNov.17,2025
-
Advantages of a Steel Portal Frame Shed
NewsNov.17,2025
-
The Erection Process of a Steel Building Hangar
NewsNov.17,2025
-
Energy Efficiency of Steel Dome Garage Kits
NewsNov.17,2025
-
Fire Resistance of Kit Metal Garages
NewsNov.17,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.