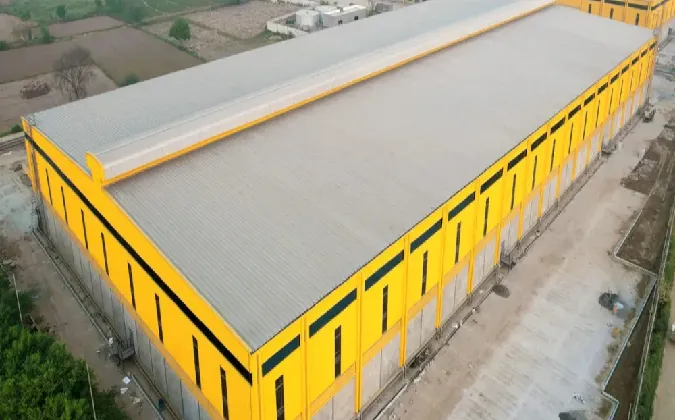
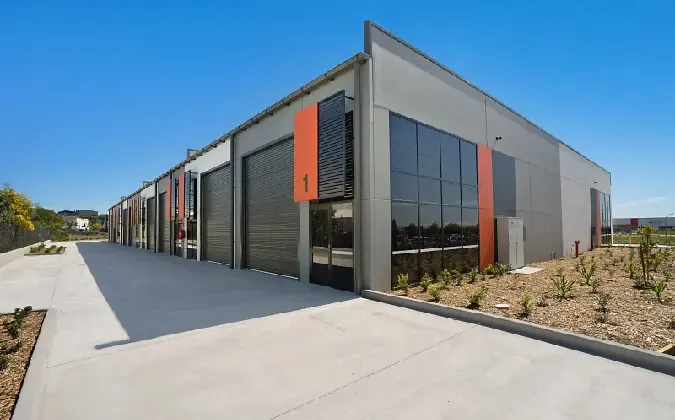
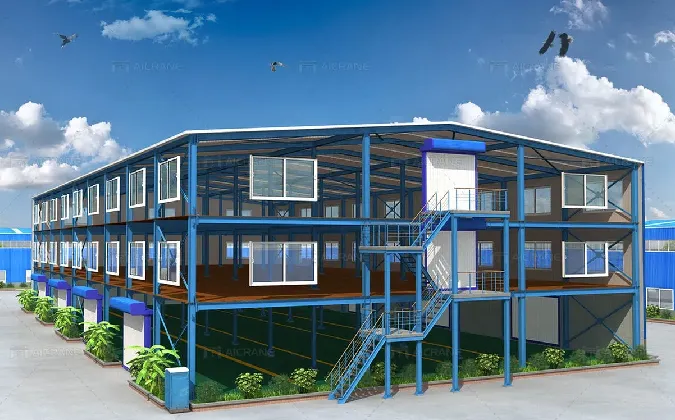
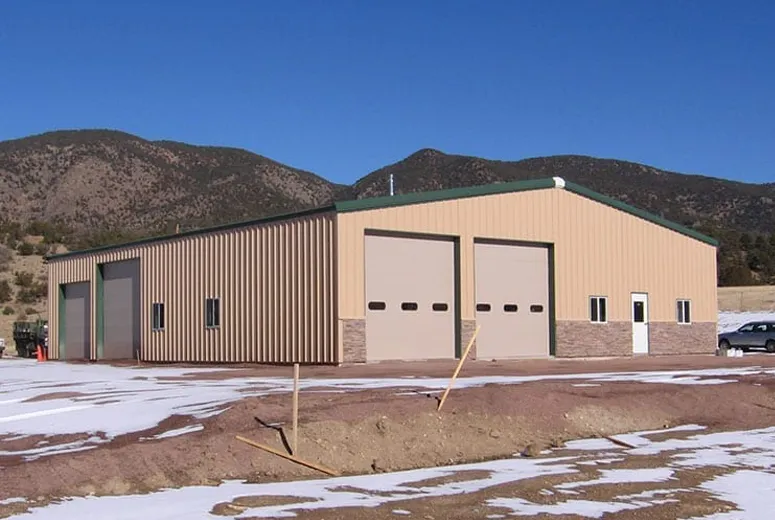
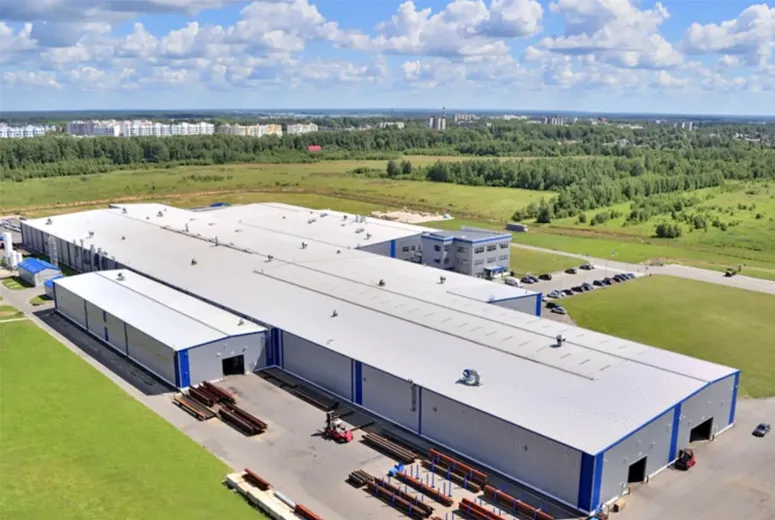
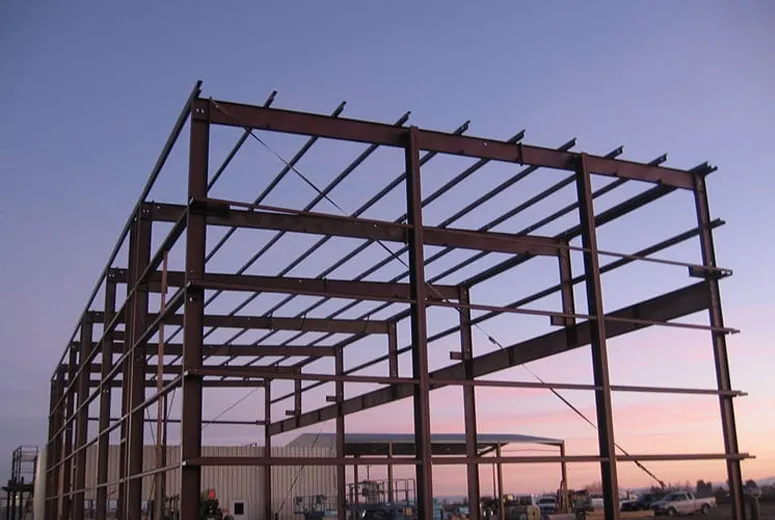
Industrial buildings are specialized structures designed to support various industrial operations such as manufacturing, warehousing, logistics, and production. These buildings are characterized by their functional design, durability, and adaptability to meet the specific needs of industrial activities.
One of the most significant features of industrial buildings is their large interior space and open floor plans. These designs enable the accommodation of heavy machinery, production lines, and storage systems without the need for intermediate supports. High ceilings and expansive layouts provide flexibility for reconfiguring spaces as operational needs evolve.
Industrial buildings are often constructed using robust materials like steel and reinforced concrete, ensuring durability and the ability to withstand heavy loads, vibrations, and other industrial stresses. These materials also enhance the structure’s resistance to environmental factors such as extreme weather and corrosion, making them ideal for long-term use.
Another key feature is the focus on efficiency and functionality. Industrial buildings typically include features like loading docks, wide access doors, advanced ventilation systems, and specialized flooring to handle heavy equipment and high-traffic movement.
Energy efficiency and sustainability are increasingly prioritized in modern industrial buildings. Green building technologies, such as solar panels, LED lighting, and energy-efficient HVAC systems, are integrated to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Lastly, customization options make industrial buildings versatile. They can be tailored to specific industries, whether it’s food processing, automotive manufacturing, or logistics hubs, ensuring optimal performance and productivity.
In summary, industrial buildings combine strength, functionality, and adaptability to support the demanding requirements of industrial operations, making them essential assets for various sectors.
The Three Types of Industrial Buildings
Industrial buildings play a crucial role in supporting diverse business operations, and they can generally be categorized into three main types: manufacturing buildings, warehouse buildings, and distribution centers. Each type serves specific industrial needs.
1. Manufacturing Buildings
These buildings are designed to house production processes, ranging from light manufacturing (e.g., assembly of small products) to heavy manufacturing (e.g., large-scale machinery and equipment production). They are equipped with heavy-duty floors, high ceilings, and ample space for machinery, raw materials, and production lines. Manufacturing buildings often include utility systems like power distribution, ventilation, and water supply to support complex industrial processes.
2. Warehouse Buildings
Warehouses are primarily used for storage and inventory management. They feature large open spaces with high ceilings to accommodate shelving systems or pallet racks. Key characteristics include loading docks, wide access points for trucks, and climate control for sensitive goods. Warehouses are essential for businesses that need to store raw materials, finished products, or spare parts efficiently.
3. Distribution Centers
Distribution centers are specialized facilities designed for quick movement of goods. They function as hubs for receiving, sorting, and shipping products to various locations. Unlike traditional warehouses, distribution centers prioritize speed and efficiency, often incorporating advanced logistics systems, conveyor belts, and automated inventory tracking technologies.
In summary, the three types of industrial buildings—manufacturing buildings, warehouse buildings, and distribution centers—cater to different aspects of industrial operations, ensuring that businesses can manage production, storage, and distribution effectively.
What is an example of an industrial building?
Warehouses are a prime example of industrial buildings, playing a pivotal role in the storage and management of goods for various industries. Designed for functionality and efficiency, warehouses support supply chain operations by providing a centralized space for storing raw materials, finished products, or intermediate goods.
A typical warehouse features large open spaces with high ceilings, allowing for vertical storage solutions such as pallet racks and shelving systems. This maximizes storage capacity while minimizing the building's footprint. Additionally, warehouses are equipped with wide loading docks and large entryways to facilitate easy loading and unloading of goods by trucks or forklifts.
Climate control systems are another key feature of modern warehouses, enabling businesses to store temperature-sensitive goods such as pharmaceuticals, food items, or electronics. Many warehouses are also integrated with advanced inventory management systems, including barcoding, RFID tracking, and automated sorting technologies, ensuring real-time monitoring and efficient stock management.
Warehouses come in various forms, including general storage warehouses, distribution warehouses, and cold storage facilities. For example, cold storage warehouses are specialized to maintain low temperatures, catering to the food and medical industries.
In summary, warehouses exemplify industrial buildings by blending structural durability, operational efficiency, and technological integration. They are indispensable assets for businesses seeking to streamline storage, safeguard products, and support seamless supply chain operations.