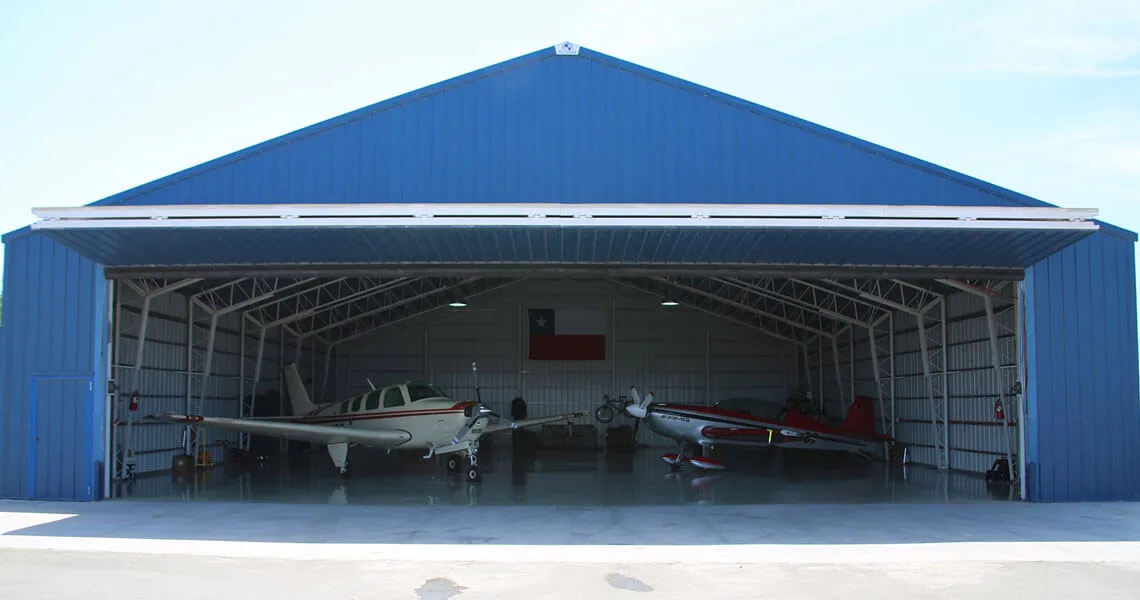
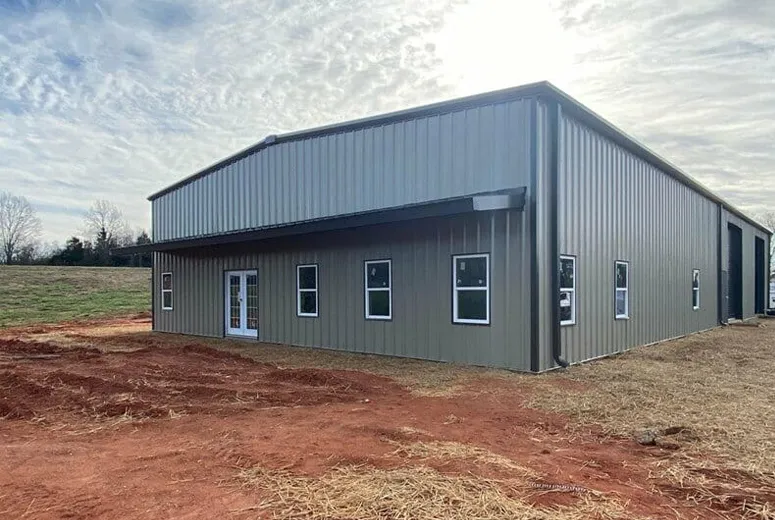
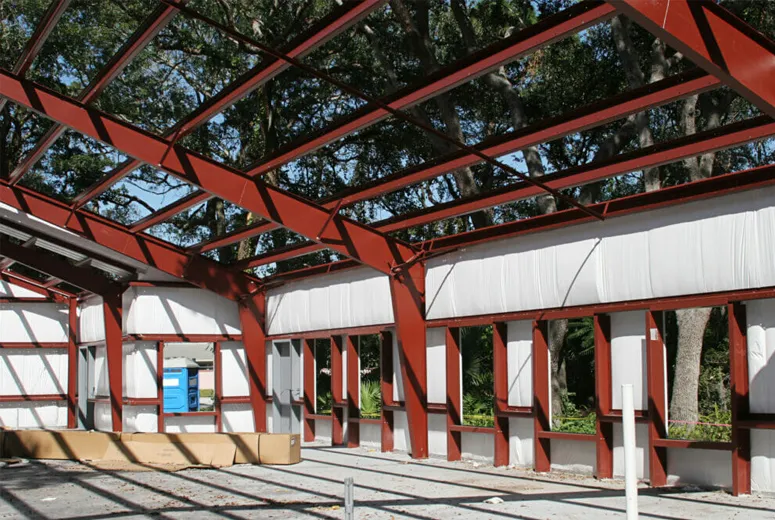
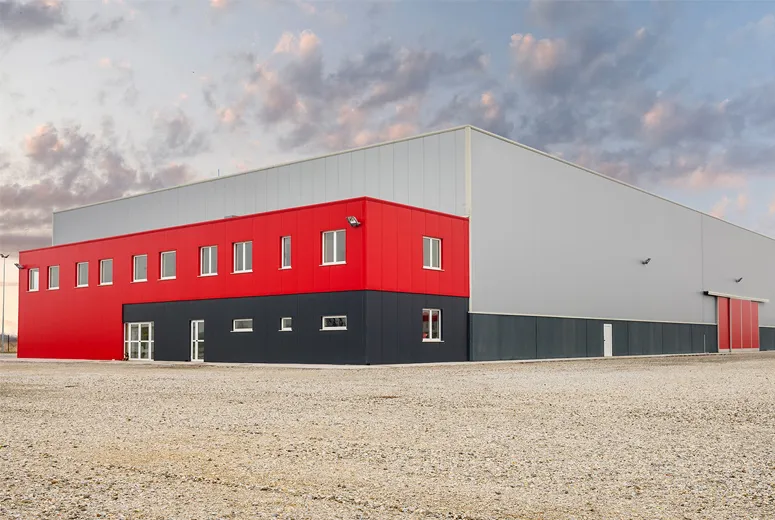
Residential steel buildings offer a modern, durable, and cost-effective solution for constructing homes. These structures combine practicality with contemporary aesthetics, making them an increasingly popular choice for homeowners seeking longevity and sustainability.
1. Durability and Strength
Steel is one of the strongest building materials, offering exceptional resistance to environmental challenges such as wind, heavy snow, and seismic activity. Residential steel buildings are also resistant to pests, mold, and fire, ensuring a long-lasting structure with minimal maintenance.
2. Versatile Design
Steel buildings can be customized to suit various architectural styles, from minimalist modern homes to traditional designs. They allow for open floor plans due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, enabling larger, uninterrupted interior spaces.
3. Energy Efficiency
Steel residential buildings can be insulated effectively, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. Many designs incorporate energy-efficient roofing and wall panels to further enhance sustainability.
4. Quick and Cost-Effective Construction
Prefabricated steel components simplify the construction process, reducing labor costs and project timelines. This makes steel buildings an economical choice compared to traditional materials like wood or concrete.
5. Eco-Friendly
Steel is 100% recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly building material. The prefabrication process also reduces waste, contributing to sustainable construction practices.
6. Low Maintenance
Unlike wood, steel does not warp, rot, or require frequent treatments, saving time and money on upkeep.
In conclusion, residential steel buildings combine durability, design flexibility, and eco-friendliness, making them an excellent option for modern living spaces.
What Grade of Steel Is Used in Residential Building?
The grade of steel used in residential buildings is chosen based on the structural requirements, safety standards, and durability needs of the project. Different types of steel are employed for framing, reinforcement, and other construction purposes.
1. Carbon Steel (Mild Steel)
Carbon steel, often referred to as mild steel, is the most commonly used grade in residential buildings. It offers a balance of strength and ductility, making it ideal for structural framing and reinforcements. Grades such as ASTM A36 or EN S235 are popular for their weldability and cost-effectiveness.
2. High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel (HSLA)
For structures requiring additional strength and resistance to environmental factors, high-strength low-alloy steel is used. HSLA grades, such as ASTM A572 or EN S355, provide superior tensile strength and durability while maintaining a relatively lightweight profile.
3. Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is frequently used for roofing, wall panels, and other exposed components. Its zinc coating provides excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity even in humid or coastal environments.
4. Stainless Steel
For specific residential applications like railings, cladding, and decorative elements, stainless steel is employed. Its high corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal make it a premium choice.
5. Reinforcing Steel (Rebar)
For concrete reinforcement, grades such as ASTM A615 or A706 are utilized. These bars ensure the structural integrity of foundations, beams, and slabs.
In conclusion, the grade of steel used in residential buildings depends on the specific application and design requirements, with carbon steel, HSLA, and galvanized steel being the most common choices for their strength, versatility, and durability.
Is It Cheaper to Build with Steel?
Building with steel can be a cost-effective option, depending on the project’s scope and requirements. While the initial material cost of steel might be higher than traditional options like wood or concrete, its long-term advantages often result in overall savings.
1. Faster Construction Time
Steel structures are typically prefabricated, which reduces construction time significantly. This efficiency translates to lower labor costs and shorter project timelines, saving money on overhead expenses.
2. Durability and Low Maintenance
Steel is highly durable, resistant to pests, fire, and environmental factors like moisture and corrosion (when treated). Its long lifespan and low maintenance requirements reduce costs over time, especially for repairs and replacements.
3. Material Efficiency
Steel’s high strength-to-weight ratio allows for lighter structures without compromising stability. This reduces the amount of material needed, lowering costs for transportation and foundation work.
4. Recyclability and Waste Reduction
Steel is 100% recyclable, and prefabricated components minimize material waste during construction. This not only supports sustainable practices but also reduces expenses associated with unused materials.
**5. Energy Efficiency**
Modern steel buildings can be designed with advanced insulation and energy-efficient features, lowering heating and cooling costs in the long run.
While steel may not always be the cheapest upfront, its benefits in speed, durability, and efficiency often make it a cost-effective choice over the building’s lifetime. For projects requiring durability and scalability, steel is an economically sound investment.