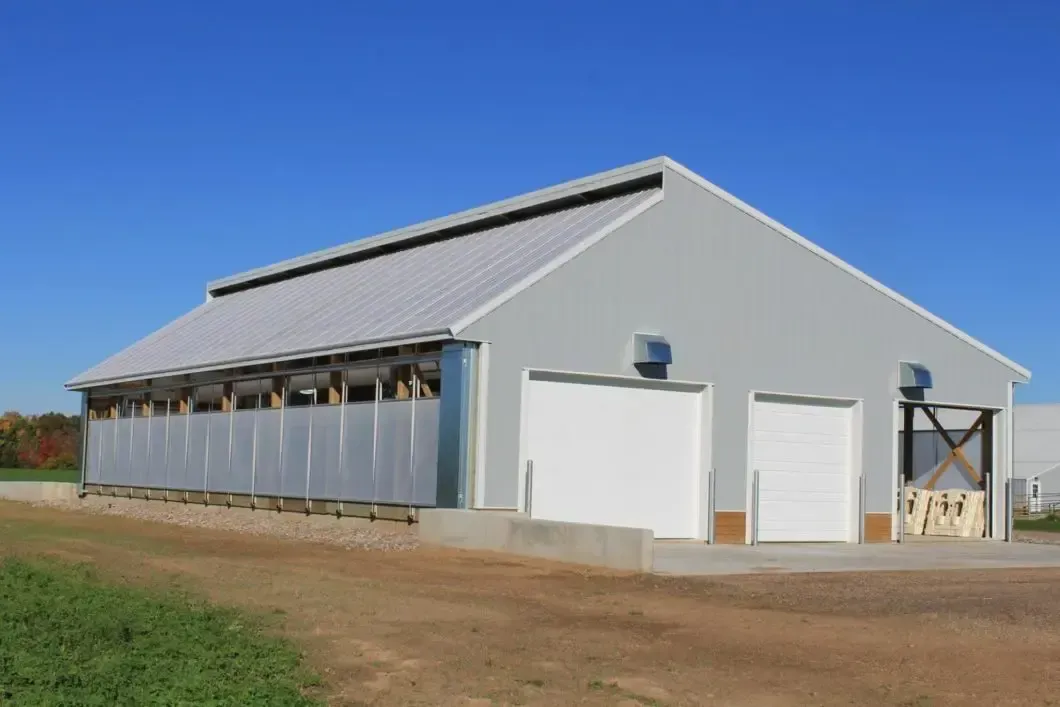
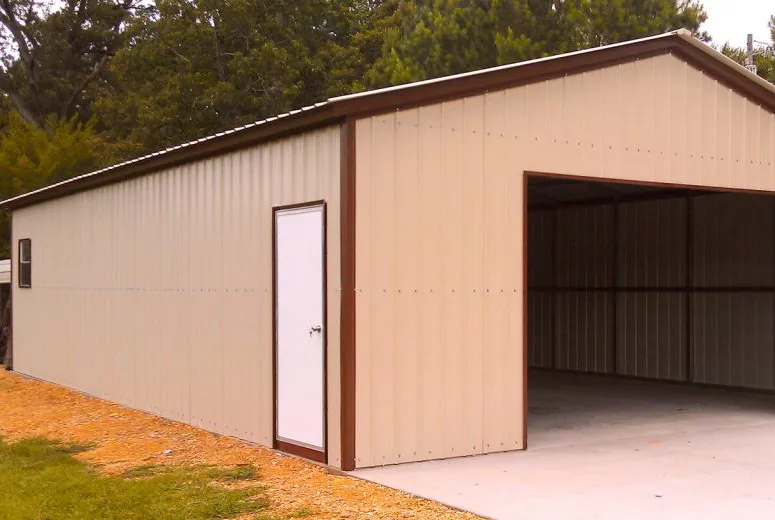
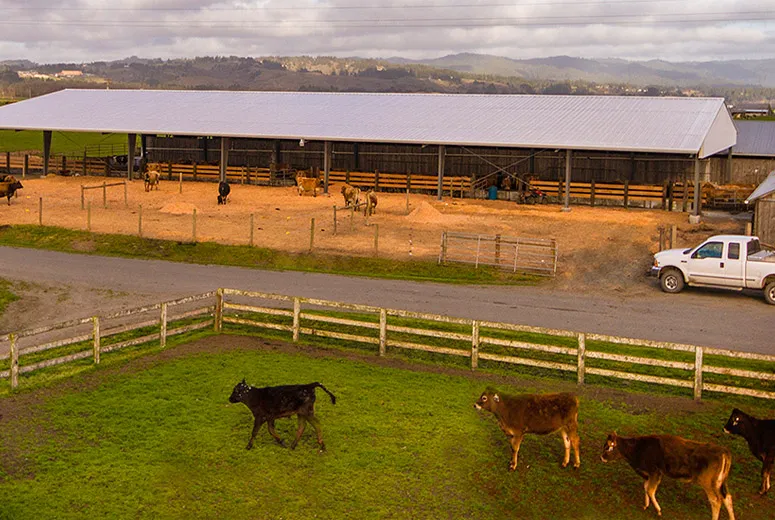
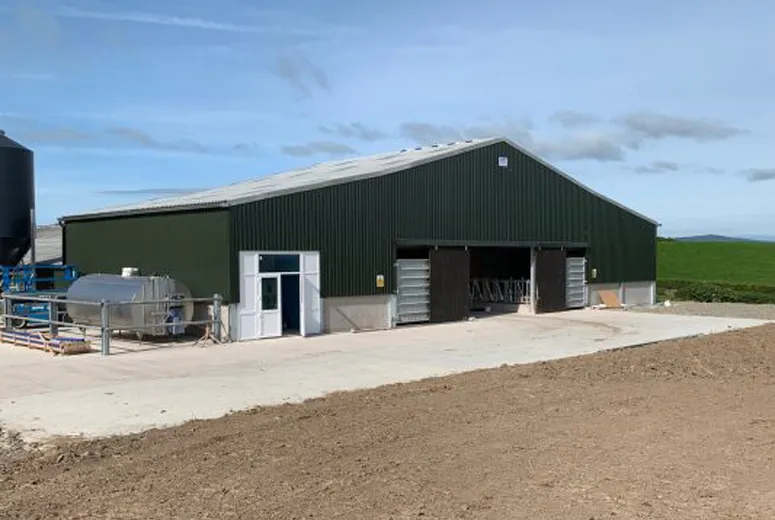
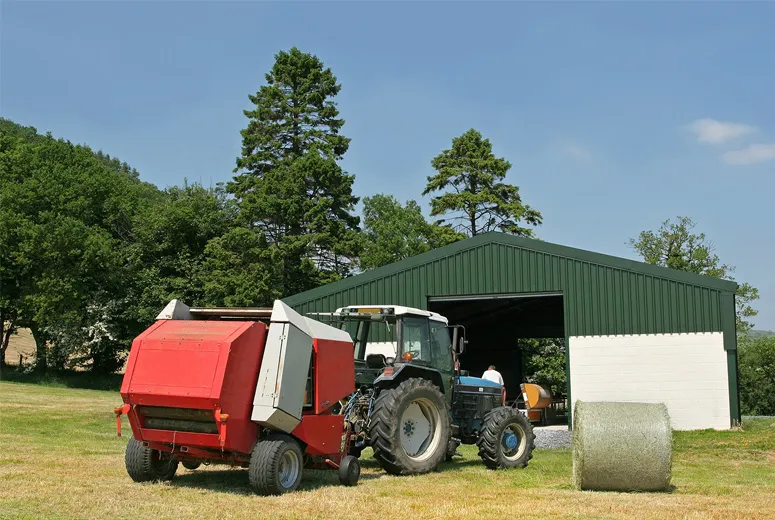
Livestock farm steel buildings are modern, efficient, and durable solutions designed to meet the needs of animal farming. These structures provide a safe and comfortable environment for livestock while offering flexibility and cost-effectiveness for farmers.
1. Durability and Weather Resistance
Constructed with high-quality steel, these buildings are built to withstand harsh weather conditions, including heavy winds, snow, and rain. Steel is resistant to pests, mold, and rot, ensuring long-term reliability and reducing maintenance costs.
2. Customizable Design
Steel livestock buildings can be customized to suit various farm needs, including housing for cattle, poultry, horses, or other animals. They can accommodate specific features such as feeding areas, ventilation systems, and storage for equipment or feed.
3. Ventilation and Climate Control
Proper airflow and temperature regulation are crucial for livestock health. Steel buildings can be equipped with ventilation systems, insulation, and heating or cooling mechanisms to maintain an optimal environment, enhancing animal welfare and productivity.
4. Quick and Cost-Effective Construction
Prefabricated steel components allow for faster assembly compared to traditional building materials. This minimizes labor costs and reduces downtime, enabling farmers to start operations sooner.
5. Easy Maintenance and Hygiene
Steel structures have smooth surfaces that are easy to clean and disinfect, promoting hygiene and reducing the risk of disease outbreaks.
6. Sustainability
Steel is a recyclable material, making livestock farm steel buildings an environmentally friendly choice. Prefabrication also minimizes waste during construction.
In conclusion, livestock farm steel buildings offer durability, versatility, and efficiency, making them an ideal solution for modern farming operations focused on animal health and productivity.
How Do You Build a Farm?
Building a farm involves careful planning, resource allocation, and the implementation of systems to meet agricultural goals. Whether for crop cultivation, livestock rearing, or mixed farming, each step is critical to ensuring a functional and sustainable operation.
1. Planning and Land Selection
The first step is to identify the type of farming you want to pursue. Choose land suitable for your farming goals, considering factors like soil quality, climate, water availability, and accessibility. Conduct a feasibility study to assess market demand, costs, and potential returns.
2. Infrastructure Development
Build essential structures such as barns, livestock shelters, storage facilities, irrigation systems, and fencing. Steel structures are popular for their durability and cost-efficiency. If livestock farming is the focus, include proper housing with ventilation and drainage systems. For crop farming, prioritize greenhouses or field irrigation setups.
3. Equipment and Supplies
Acquire the necessary machinery and tools, such as tractors, plows, and harvesters. For livestock farming, ensure you have feeding systems, water tanks, and medical supplies.
4. Resource Management
Develop efficient systems for water management, soil enrichment, and waste disposal. Incorporate sustainable practices like crop rotation, composting, or renewable energy sources to minimize environmental impact.
5. Hiring and Training
Hire skilled labor and provide training on farming techniques and equipment use. Knowledge of modern farming practices and technology can enhance productivity.
6. Operations and Marketing
Start with small-scale operations and expand gradually. Develop marketing channels for selling produce, such as local markets, wholesale buyers, or direct-to-consumer platforms.
Building a farm requires dedication, planning, and adaptability, but with the right strategies, it can become a rewarding and sustainable venture.
What Is a House Built on a Farm with Buildings Around It?
A house built on a farm with surrounding buildings is commonly referred to as a farmstead. This central structure typically serves as the farmer's residence, while the adjacent buildings are designed to support various agricultural activities. Together, they form a functional and efficient setup for managing farm operations.
1. The Farmhouse
The farmhouse is the primary residential building on the farm, where the farmer and their family reside. It is often designed for comfort and practicality, considering the demands of farm life. Modern farmhouses may also incorporate traditional architectural elements to reflect rural charm.
2. Outbuildings
Surrounding the farmhouse are essential structures such as barns, stables, storage sheds, silos, and garages. These buildings serve specific purposes, including housing livestock, storing crops or equipment, and protecting machinery from the elements.
3. Functional Layout
A farmstead is strategically designed to ensure efficiency. The layout often positions the farmhouse at the center for easy access to outbuildings and fields. Pathways and open spaces facilitate movement of machinery and livestock.
4. Community and Sustainability
Historically, farmsteads were hubs of self-sufficiency, supporting the family's needs while contributing to local economies. Today, modern farmsteads blend traditional values with sustainable practices, including renewable energy and eco-friendly designs.
In conclusion, a house built on a farm with buildings around it is more than just a residence; it is the heart of the farm, providing a harmonious balance between living spaces and agricultural functionality.