- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Dec . 07, 2024 15:16 Back to list
Building Steel Design An Overview of Principles and Applications
Steel has long been a favored material in construction due to its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, versatility, and durability. The design of steel structures is a critical aspect of civil engineering and architecture, where safety, aesthetics, and functionality are paramount. This article explores the principles of building steel design, discusses its applications, and highlights essential considerations in the design process.
Principles of Steel Design
At the core of steel design are fundamental engineering principles that ensure structures can withstand various loads, resist environmental factors, and maintain their integrity over time. The key principles include
1. Load Consideration Structures must be designed to support various loads, including dead loads (permanent static weights), live loads (temporary dynamic weights), environmental loads (wind, seismic activity, snow), and other operational loads. Comprehensive load analysis is crucial in determining the required strength and stability of the steel components.
2. Material Properties Steel is selected for its properties such as yield strength, ductility, and toughness. Understanding these properties allows engineers to choose the appropriate steel grades for specific applications, ensuring the structure can perform under anticipated conditions.
3. Structural Analysis Engineers employ various analytical methods, including finite element analysis and traditional methods of load path analysis, to predict how steel elements will behave under load. This analysis helps in determining the optimal shapes and sizes of steel members.
4. Design Codes and Standards Compliance with established design codes and standards, such as the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) standards and Eurocodes, is vital. These guidelines provide specifications for material strength, safety factors, and design procedures, ensuring consistent and safe results across projects.
5. Connection Design Connections are critical in steel structures, as they transfer loads between members. Different connection types, such as welded, bolted, or riveted, are designed based on the load requirements and structural configuration. Effective connection design is essential for structural integrity and reliability.
Applications of Steel Design
Steel structures are prevalent across various sectors due to their adaptability and efficiency. Some common applications include
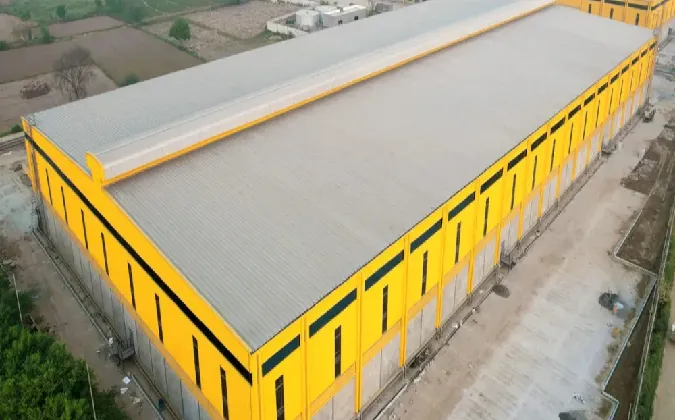
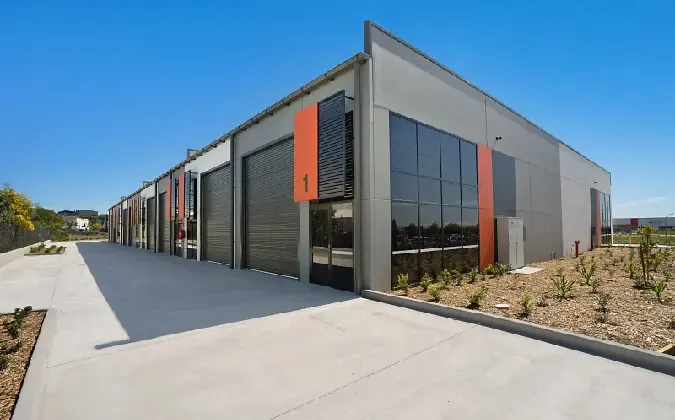
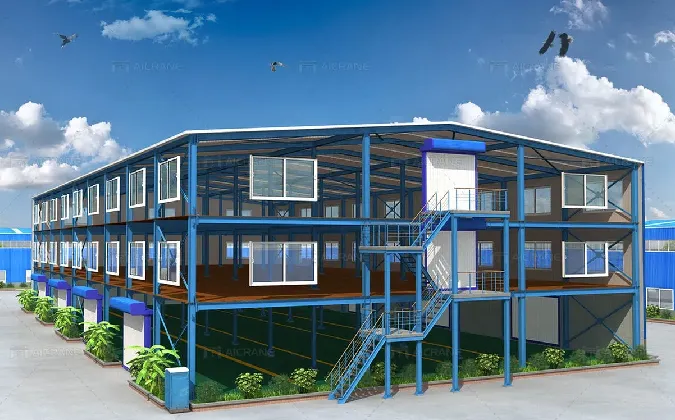
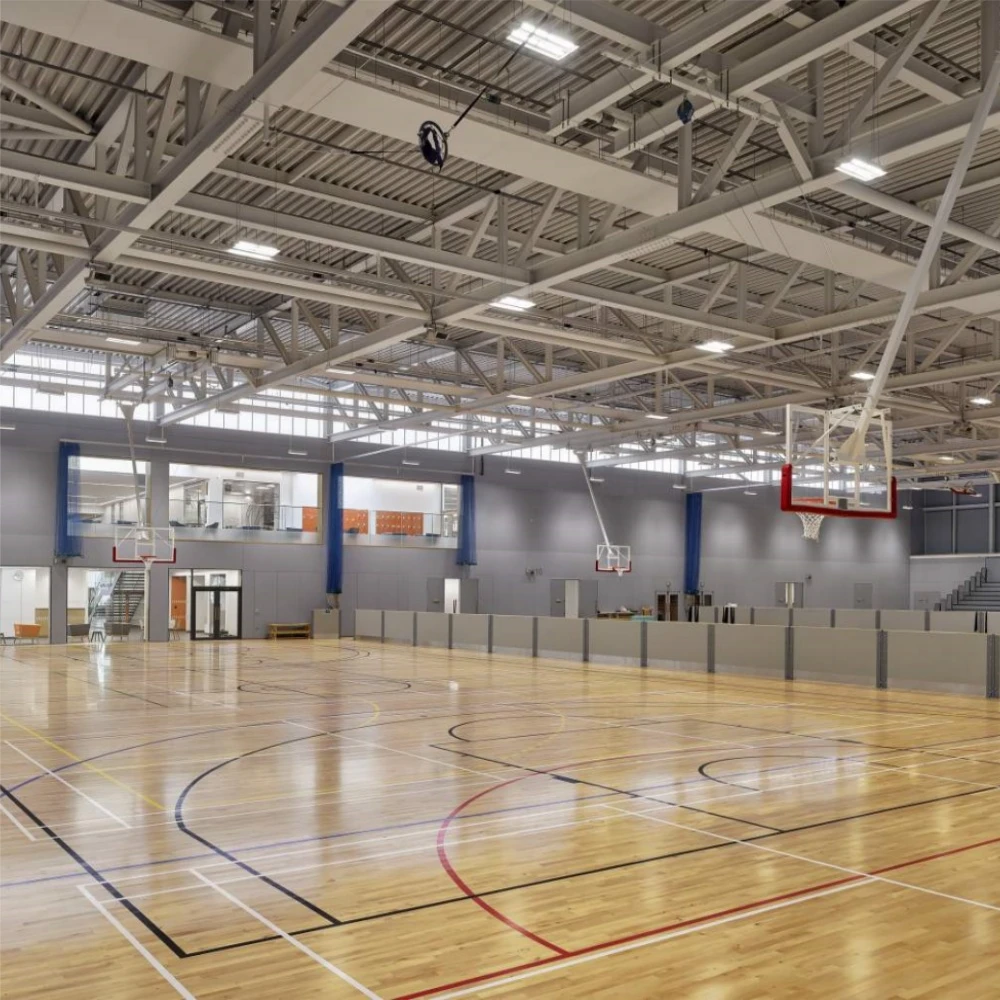
1. Buildings Skyscrapers and commercial buildings often use steel frames to achieve height and open spaces. Steel allows for large spans and fewer columns, providing flexibility in interior layouts.
building steel design

2. Bridges Steel bridges are crucial in transportation infrastructure. Their high strength and lightweight characteristics make them suitable for long spans and complex geometries, ensuring safety and functionality.
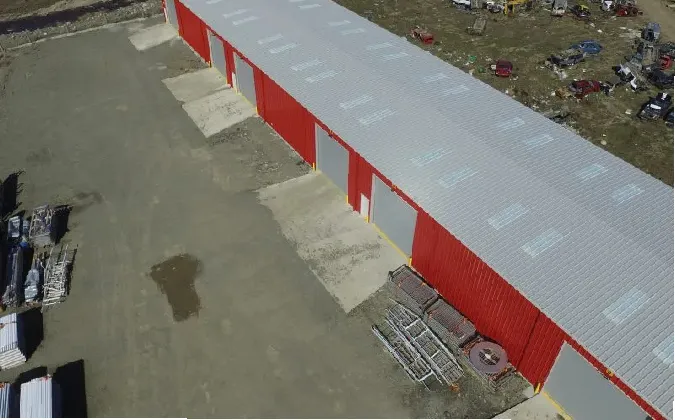
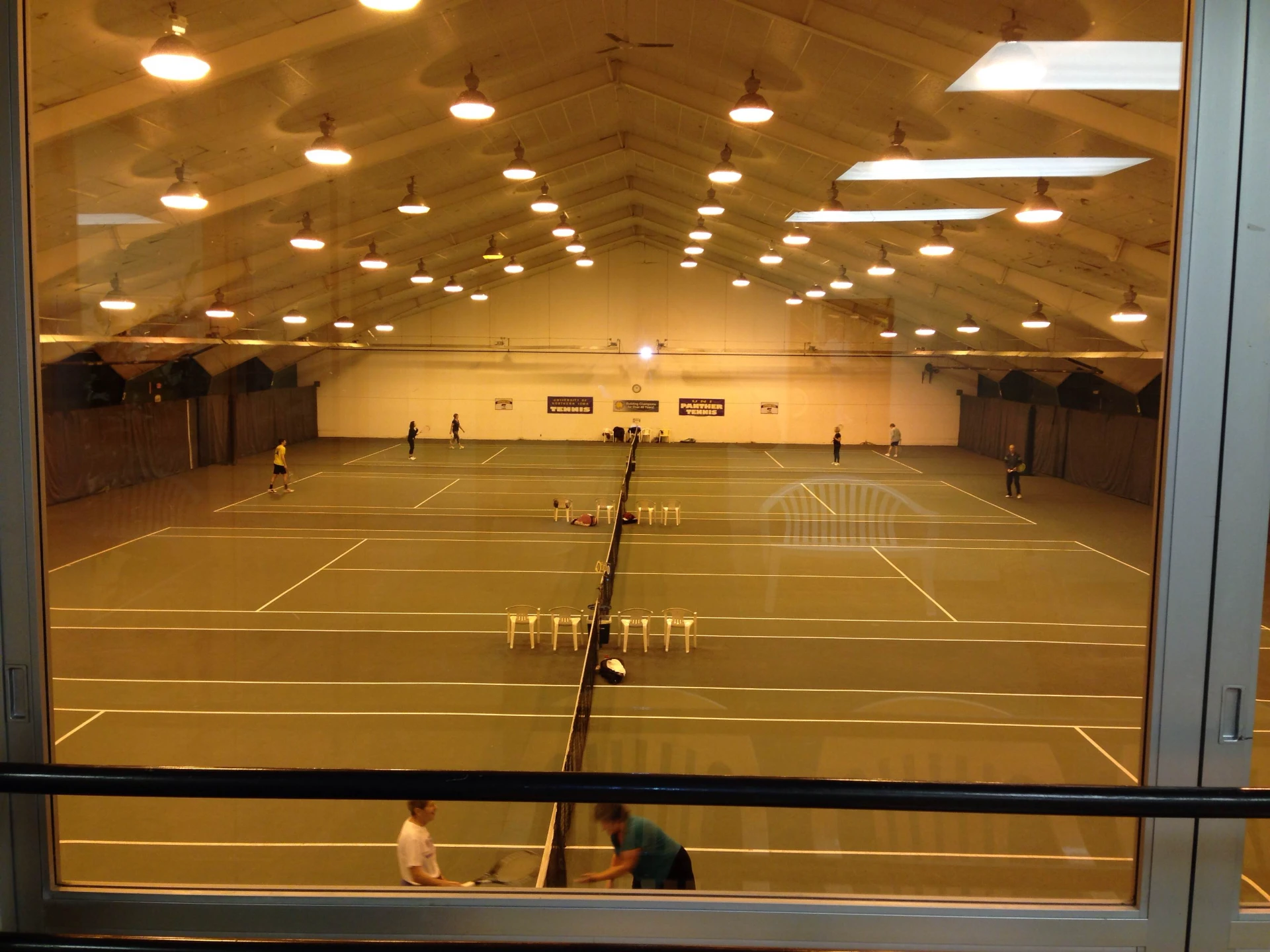
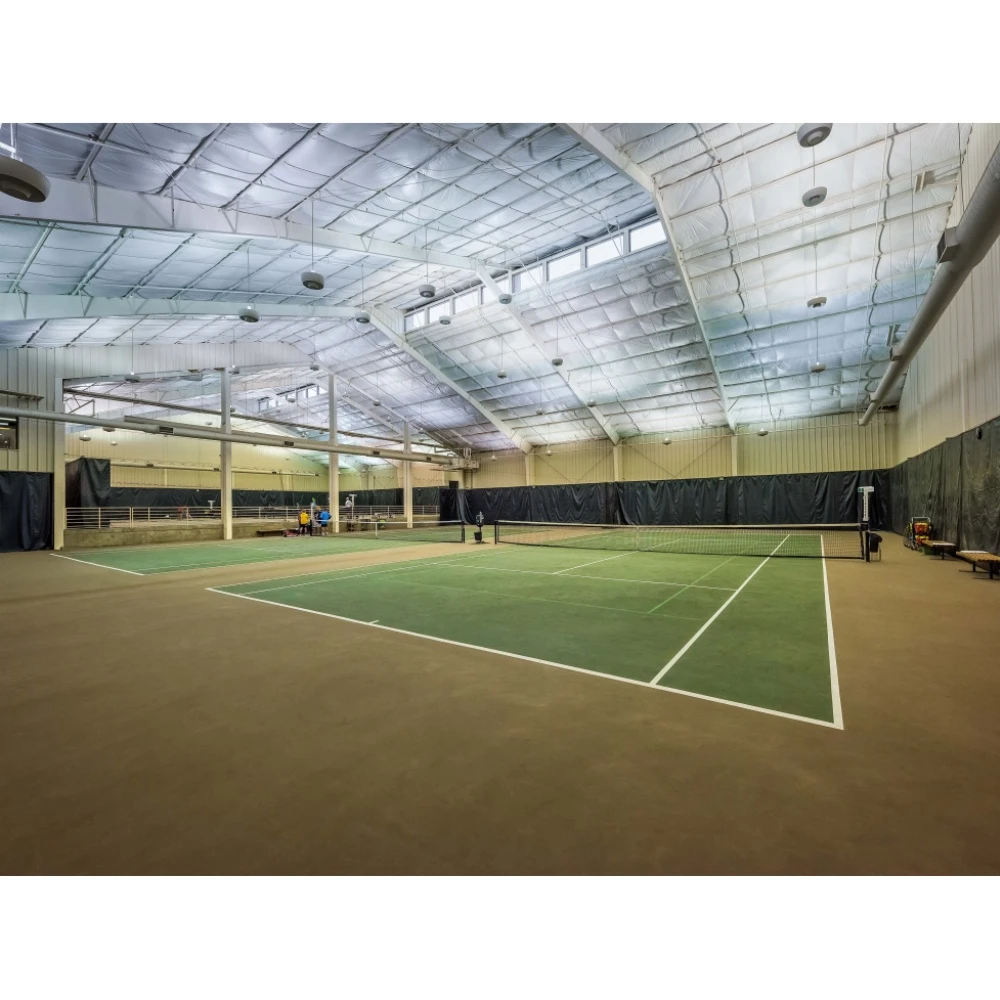
3. Industrial Structures Factories and warehouses benefit from steel's durability and ease of construction. Steel structures can accommodate heavy machinery and high loads, making them ideal for industrial uses.
4. Marine and Offshore Structures Steel is the material of choice for constructing platforms, ships, and other marine structures due to its resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Considerations in Steel Design
While steel offers numerous advantages, several considerations must be addressed in the design process
1. Corrosion Protection Steel is susceptible to corrosion, which can compromise structural integrity. Protecting steel through coatings, galvanization, or using stainless steel can enhance durability.
2. Sustainability With growing environmental concerns, the sustainability of steel production and its lifecycle considerations are increasingly important. Engineers are adopting green practices, such as using recycled steel, to minimize the environmental impact.
3. Cost Efficiency Economic factors play a significant role in material selection and design choices. Balancing safety, functionality, and cost-effectiveness is essential for successful project delivery.
4. Innovative Technologies Advancements in technology, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and advanced fabrication methods, have revolutionized steel design. These technologies enable greater precision, efficiency, and the ability to handle complex geometries.
Conclusion
Building steel design is a sophisticated process that integrates engineering principles, material science, and architectural considerations. With its unparalleled strength, flexibility, and adaptability, steel remains a material of choice for modern construction. As the industry evolves, ongoing innovations and a focus on sustainability will continue to shape the future of steel structures, ensuring they meet the demands of urban development and infrastructure needs for generations to come.
-
How Do Prefabricated Steel Structures Transform Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefabricated Metal Buildings Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefab Insulated Metal Buildings and Steel Structures Revolutionize Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Pre - Engineered Steel Structures Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Modular Construction with Prefabricated Metal Structures
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Industrial Infrastructure with Prefabricated Steel Solutions
NewsJul.14,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.