- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Nov . 07, 2024 20:56 Back to list
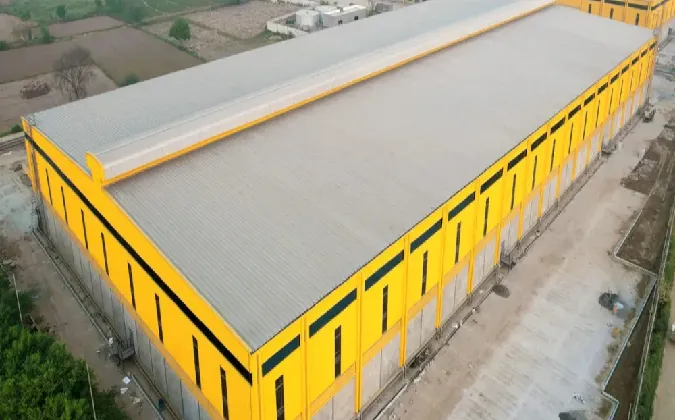
Cold-Formed Steel Structures An Overview
Cold-formed steel (CFS) structures have gained immense popularity in the construction industry in recent years due to their unique properties, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. CFS refers to steel sections that are formed at room temperature, typically through a series of cold-working processes that enhance their strength and ductility. Such structures are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, providing a robust framework that is both lightweight and durable.
One of the primary advantages of cold-formed steel is its high strength-to-weight ratio. This characteristic allows for the construction of lighter structures without compromising structural integrity. It minimizes the dead load on foundations and makes handling and transportation more efficient. Additionally, these materials can be produced in various shapes and sizes, catering to diverse architectural designs and engineering requirements.
Cold-Formed Steel Structures An Overview
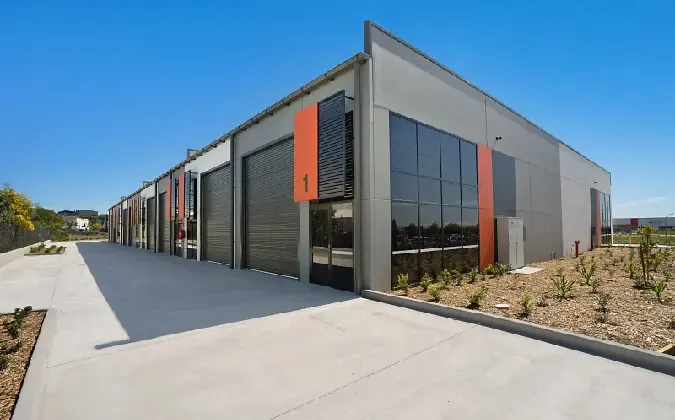
Moreover, CFS structures are highly adaptable, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They are used in the construction of load-bearing walls, floors, and roofs, providing a versatile option for builders. The ease with which CFS can be cut, shaped, and assembled allows for innovative designs and construction methodologies. Prefabrication techniques further enhance this adaptability, allowing components to be manufactured off-site in controlled environments and then assembled on-site, leading to time savings and reduced labor costs.
cold formed steel structures
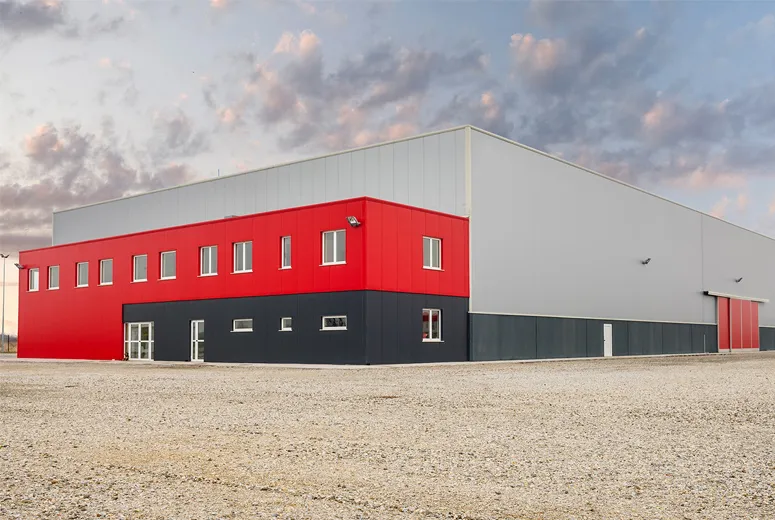

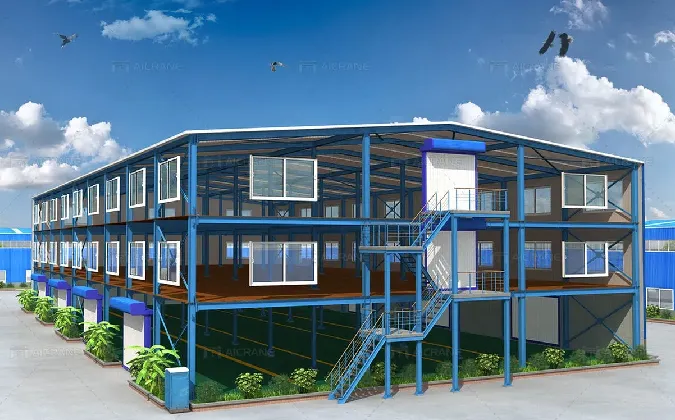
Designing with cold-formed steel involves various considerations, including load-bearing capacity, buckling resistance, and connections. Engineers use sophisticated software for modeling and analyzing CFS structures to ensure they meet the required performance standards and building codes. The implementation of standardized design methodologies, such as those outlined by the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI), provides guidelines that enhance safety and efficiency in the design process.
However, there are challenges associated with CFS construction that must be addressed. One significant challenge is the potential for local buckling, which can occur when the steel sections are subjected to excessive loads. To counter this, engineers must carefully consider the thickness and dimensions of the sections and design reinforcements as necessary. Furthermore, precise detailing of connections is crucial for maintaining structural integrity, as these points are often the weakest areas of a structure.
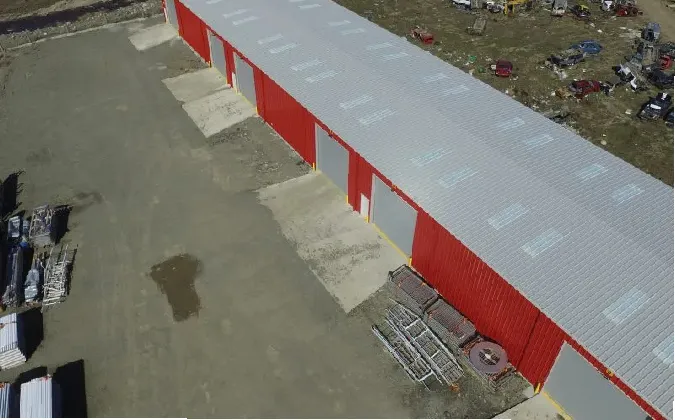
Sustainability is another key aspect of cold-formed steel structures. Steel is a highly recyclable material, and incorporating recycled content into production can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of CFS construction. The use of CFS aligns with today’s push for more sustainable building practices, minimizing waste and promoting resource efficiency.
In conclusion, cold-formed steel structures represent an innovative and efficient solution in modern construction. Their lightweight design, durability, and versatility make them suitable for a variety of applications. While there are challenges to consider, advancements in engineering and design practices continue to enhance their performance and sustainability. As the construction industry evolves, the significance of cold-formed steel is likely to grow, paving the way for more sustainable and resilient buildings in the future.
-
How Do Prefabricated Steel Structures Transform Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefabricated Metal Buildings Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefab Insulated Metal Buildings and Steel Structures Revolutionize Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Pre - Engineered Steel Structures Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Modular Construction with Prefabricated Metal Structures
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Industrial Infrastructure with Prefabricated Steel Solutions
NewsJul.14,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.