- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Sep . 25, 2024 15:56 Back to list
Cold-Formed Steel Structures An Overview
Cold-formed steel (CFS) structures have gained significant traction in modern construction due to their versatility, efficiency, and sustainability. Utilizing thin steel sheets, these structures are shaped at room temperature through various processes, rendering them lightweight yet robust. As the demand for innovative building solutions rises, understanding the advantages and applications of cold-formed steel becomes crucial for architects, engineers, and builders alike.
Understanding Cold-Formed Steel
Cold-formed steel is produced by rolling or bending metal sheets into desired shapes without applying heat, which differentiates it from hot-formed steel that undergoes heating in the manufacturing process. The CFS members are typically less than 1/4 inch thick and are renowned for their superior strength-to-weight ratio, making them exceedingly efficient for structural applications. Furthermore, CFS can be manufactured in numerous profiles such as channels, angles, and studs that contribute to the diverse applications of this material.
Advantages of Cold-Formed Steel Structures
One of the most significant benefits of cold-formed steel structures is their lightweight nature. This characteristic considerably reduces the load on supporting structures, allowing for easier handling and transport. Contrary to traditional heavy materials like timber or concrete, CFS simplifies construction logistics and reduces labor costs. Moreover, lighter materials can lead to reduced foundation requirements, minimizing overall project costs.
Sustainability is another key advantage of CFS. Steel is recyclable, and with the increasing emphasis on environmentally friendly practices in construction, using cold-formed steel aligns with green building principles. This aspect not only appeals to environmentally conscious clients but also meets various sustainability standards and certifications, making it a favorable choice in today’s eco-aware market.
Versatility in Design and Application
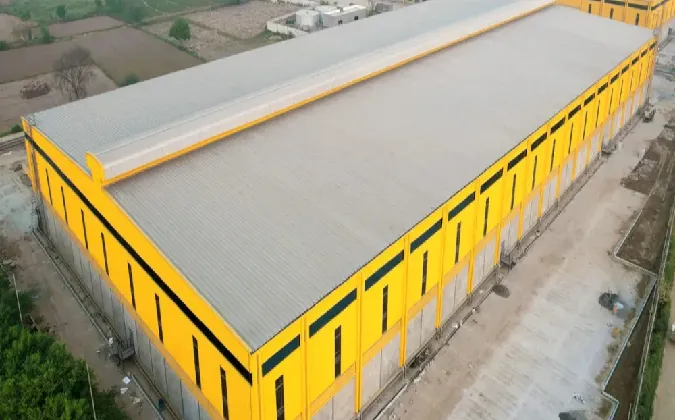
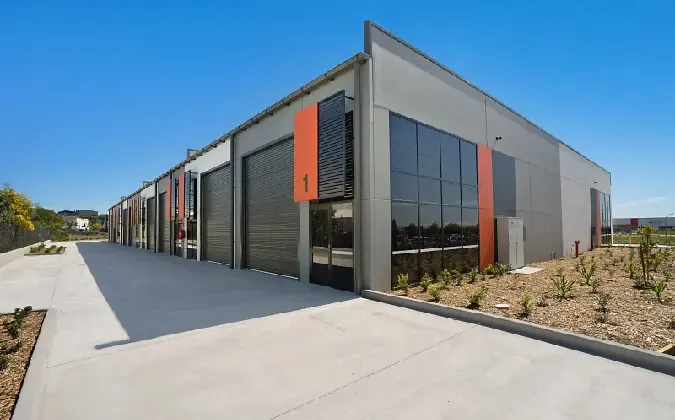
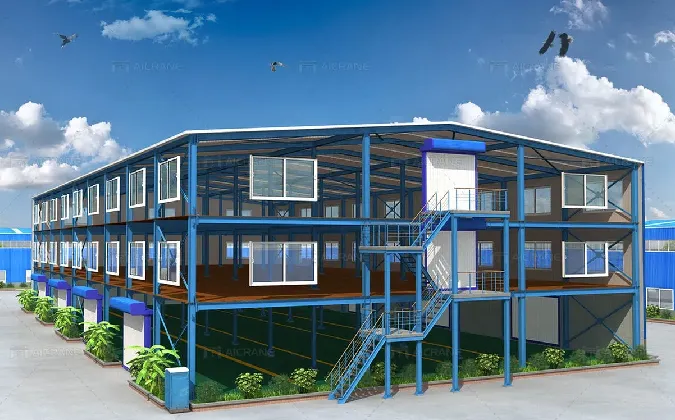
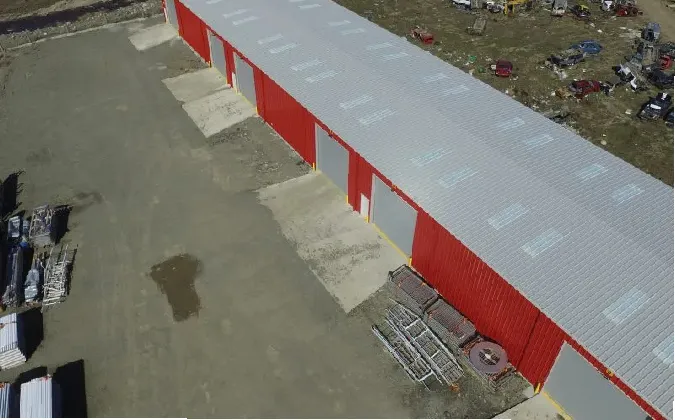
cold formed steel structures
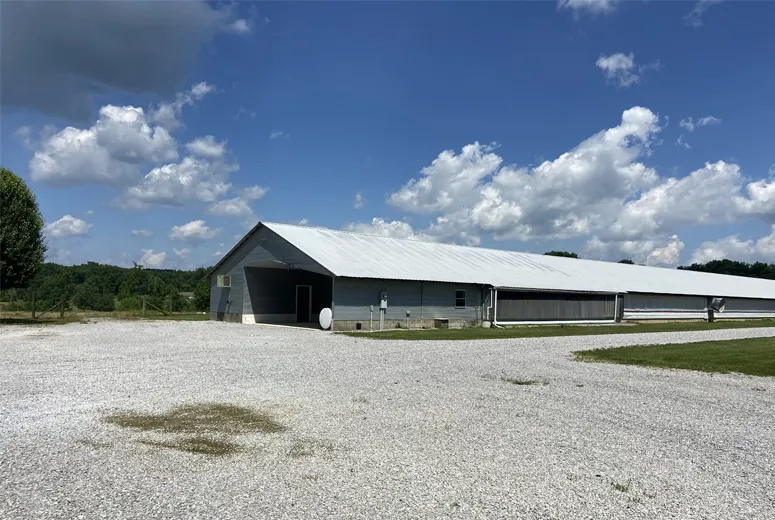

Cold-formed steel is highly versatile, accommodating an array of design needs. Its flexibility in design enables architects to create intricate shapes and patterns while maintaining structural integrity. This adaptability is particularly beneficial when designing non-standard or unique structures. Whether used in residential, commercial, or industrial applications, CFS can meet the specific requirements of various projects, including framing systems, roofing, flooring, and even façades.
Cold-formed steel structures also demonstrate excellent durability and resistance to various environmental factors. Unlike timber, CFS is impervious to pests, rot, and mold, ensuring longevity with minimal maintenance. Additionally, it exhibits resistance to fire, enhancing the safety of the building occupants. Such attributes make CFS an ideal choice for projects requiring high performance under challenging conditions.
Building Codes and Standards
As the use of cold-formed steel structures becomes more prevalent, numerous building codes and engineering standards have been developed to ensure safety and reliability. Organizations such as the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) and the International Building Code (IBC) provide guidelines for designing and constructing with CFS. Adhering to these standards is vital for ensuring that CFS structures can withstand typical loads and resist potential failures.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many advantages, CFS does not come without challenges. One notable concern is its susceptibility to corrosion, especially in humid or coastal environments. Proper protective measures, such as galvanization or the application of protective coatings, are essential to prolong the lifespan of CFS structures. Additionally, engineers must account for the material's stiffness and buckling potential in their designs, as these factors can influence the performance of the structure under loads and stress.
Conclusion
Cold-formed steel structures represent a forward-thinking approach in construction, blending efficiency, strength, and adaptability. By leveraging the advantages of this material, architects and builders can create innovative designs that meet contemporary demands while adhering to sustainability practices. As building codes evolve and technology advances, the role of cold-formed steel is likely to become even more prominent in the construction industry, paving the way for a future where versatility and resilience are fundamentally intertwined in structural design. As we look ahead, embracing the potential of cold-formed steel will undoubtedly facilitate the evolution of building practices in line with modern requirements.
-
Steel Frame Factory with Insulated Roof Panels
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Prefab Metal Building with Insulation Package Options
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Industrial Steel Sheds for Temporary Workshop Use
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Metal Workshops Featuring Corrugated Steel Roofs
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Modular Steel Frame Excellence: Our Pursuit of Perfection
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Metal Garage Kits Crafted with Customer Satisfaction at Heart
NewsAug.14,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.