- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Feb . 28, 2025 14:31 Back to list
Factory buildings are the backbone of the manufacturing sector, providing essential spaces where production, assembly, and distribution occur. Whether you're establishing a new manufacturing plant or renovating an existing one, understanding factory building types, their design considerations, and their various uses is crucial for creating a functional and efficient production environment. This guide will take you through the key elements to consider when planning a factory building.
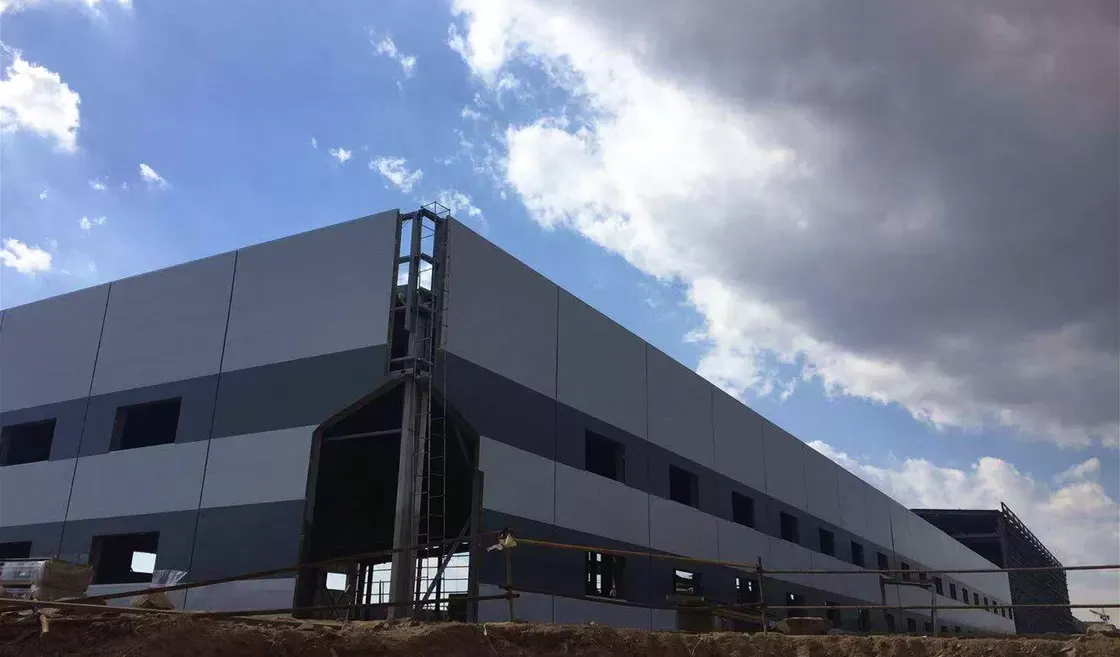

What Is a Factory Building?
A factory building is a structure used primarily for manufacturing, assembling, processing, or storing products. These buildings are specifically designed to house heavy machinery, provide adequate space for workforces, and comply with safety regulations. Factory buildings vary greatly in size, shape, and layout depending on the industry, type of production, and business needs.
Common Types of Factory Buildings
There are several types of factory buildings, each designed for specific industrial processes. The design and layout can vary greatly depending on the type of production being carried out. Below are some of the most common factory building types:
1. Single-Story Factory Buildings
These are the most common type of factory buildings, especially for light manufacturing or assembly processes. Single-story factory buildings feature a spacious, open floor plan, making them ideal for businesses that require large floor spaces for equipment or production lines.
Key Features:
- Large, open spaces without internal walls or obstructions.
- High ceilings to accommodate large machinery or cranes.
- Easy movement of materials and products through the facility.
Use Cases:
- Light manufacturing
- Assembly lines
- Warehousing and distribution
2. Multi-Story Factory Buildings
Multi-story factory buildings are typically used for operations that require separate floors for different production processes or departments. These buildings maximize vertical space, allowing for more efficient use of land in urban or limited-space locations.
Key Features:
- Several floors dedicated to different functions (e.g., manufacturing on one floor, offices on another).
- Requires industrial elevators or lifts for moving goods between floors.
- Better suited for compact urban locations where land is limited.
Use Cases:
- Textile and garment manufacturing
- High-tech industries requiring specialized labs or office spaces
- Pharmaceutical or chemical manufacturing
3. Modular Factory Buildings
Modular factory buildings are prefabricated structures that can be customized and expanded as needed. These buildings are assembled on-site, with modules that can be reconfigured or added to depending on the company’s needs.
Key Features:
- Flexible and scalable design.
- Quicker construction times compared to traditional buildings.
- Suitable for temporary or semi-permanent operations.
Use Cases:
- Small-scale manufacturing
- Startups or pilot projects
- Temporary manufacturing facilities for specific contracts
4. Steel Frame Factory Buildings
Steel frame factory buildings use a steel skeleton for support, offering a high level of durability and resistance to harsh weather conditions. This type of construction is commonly used for factories involved in heavy manufacturing or industries that require large, open spaces for machinery.
Key Features:
- High strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for large open spans.
- Durability and resistance to fire, weather, and other industrial stresses.
- Typically used for heavy industrial applications.
Use Cases:
- Automotive or aerospace manufacturing
- Large-scale metalworking and assembly operations
- Food processing and packaging plants
5. Warehouse-Style Factory Buildings
While not always classified as factories, warehouse-style buildings often serve as the production floor for companies involved in large-scale storage or logistics operations. These buildings are designed to store raw materials, finished goods, and products, while also serving as assembly or packing areas.
Key Features:
- Large open floor plans designed for storage.
- High ceilings to accommodate large palletized stock or machinery.
- Often includes loading docks for easy delivery and shipment.
Use Cases:
- Warehousing and logistics
- Order fulfillment and packaging
- Distribution centers
Factory Building Design Considerations
The design of a factory building depends on several factors, including the nature of the business, the production process, and budget. When designing or planning a factory building, consider the following elements:
1. Workflow and Layout
The layout of the factory should facilitate efficient movement of materials, products, and workers. A well-organized floor plan can reduce operational bottlenecks and increase productivity. Key considerations include:
- Optimizing the placement of machines and workstations to reduce material handling time.
- Ensuring smooth flow from raw material reception to production to finished product storage and shipment.
- Incorporating adequate safety measures to prevent accidents.
2. Structural Integrity
The structure of the factory should be designed to support the machinery and equipment it will house. The foundation must be solid, and the building materials should be durable enough to withstand the stresses from heavy machinery or production processes.
- Reinforced floors for heavy machinery.
- High-quality materials like steel for strength and durability.
- Compliance with local building codes and industrial regulations.
3. Lighting and Ventilation
Proper lighting and ventilation are critical to ensuring that workers can perform their tasks safely and efficiently. Depending on the type of work, different areas of the factory may need different lighting conditions:
- Bright, even lighting for assembly lines and production areas.
- Specialized lighting for detailed work, such as quality inspection or packaging.
- Adequate ventilation and air quality systems to maintain a safe working environment.
4. Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is an important factor in factory building design. Incorporating eco-friendly features like energy-efficient HVAC systems, natural lighting, and renewable energy sources can reduce operational costs in the long term.
- Insulation to reduce energy consumption.
- Solar panels or other renewable energy systems.
- Rainwater harvesting or greywater systems for non-potable uses.
5. Safety Standards
Factory buildings must comply with safety regulations to ensure the well-being of employees. Safety features such as fire exits, emergency lighting, fire suppression systems, and first aid stations should be integral parts of the design.
Factory Building Use
Factory buildings serve various purposes, depending on the industry and the type of manufacturing. Some common uses of factory buildings include:
1. Production
The most common use of a factory building is to house production lines where raw materials are transformed into finished goods. This includes manufacturing of products ranging from electronics to consumer goods.
2. Warehousing and Storage
Many factories also have storage sections for raw materials, finished products, or spare parts. Proper organization within these spaces is essential for inventory control and operational efficiency.
3. Quality Control and Research
Certain factory buildings, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals or automotive manufacturing, require spaces dedicated to quality control and research. These areas are equipped with specialized labs and testing equipment to ensure products meet required standards.
4. Offices
In modern factory buildings, a portion of the space is often allocated for administrative purposes, including offices for management, human resources, and other departments. In some cases, these offices are integrated into the factory building, while in others, they may be housed in separate, attached buildings.
Understanding factory building types, their design considerations, and their diverse uses is essential when planning any industrial project. Whether you need a single-story factory building for light manufacturing, a steel-frame facility for heavy industry, or a modular space for a growing business, the right design will contribute significantly to your operational success. By carefully considering factors such as layout, safety, workflow, and budget, you can create a factory building that meets your business's needs and supports long-term growth.
-
Steel Frame Factory with Insulated Roof Panels
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Prefab Metal Building with Insulation Package Options
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Industrial Steel Sheds for Temporary Workshop Use
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Metal Workshops Featuring Corrugated Steel Roofs
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Modular Steel Frame Excellence: Our Pursuit of Perfection
NewsAug.14,2025
-
Metal Garage Kits Crafted with Customer Satisfaction at Heart
NewsAug.14,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.