- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Nov . 14, 2024 18:37 Back to list
Understanding Factory Building Types A Comprehensive Overview
In the modern industrial landscape, the significance of factory buildings cannot be overstated. These structures serve as the backbone of production, housing machinery, equipment, and personnel essential for manufacturing various goods. The design and construction of factory buildings are influenced by a myriad of factors, including the type of production process, the nature of the products being manufactured, and logistical considerations. This article delves into various factory building types, highlighting their characteristics, advantages, and considerations for construction.
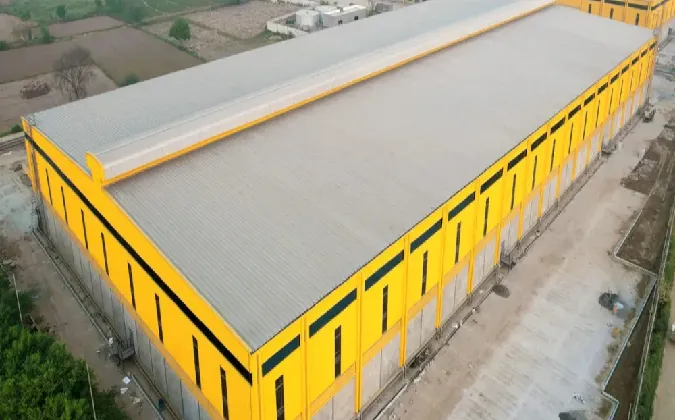
1. Single-Story Factories
Single-story factories are among the most common types of manufacturing buildings. These structures have a straightforward design, typically featuring large open spaces without intermediary floors. This layout allows for efficient movement of materials and machinery, facilitating a seamless workflow. For industries that require heavy machinery or large equipment, single-story buildings provide the necessary space and support.
Advantages - Easy access for loading and unloading goods. - Enhanced safety due to fewer stairs and elevators. - Reduced construction and maintenance costs.
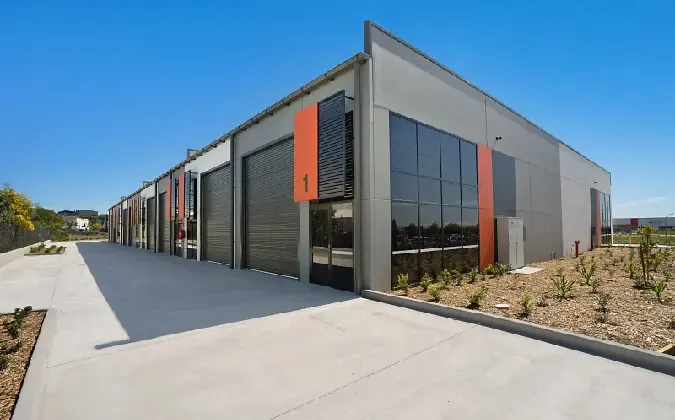
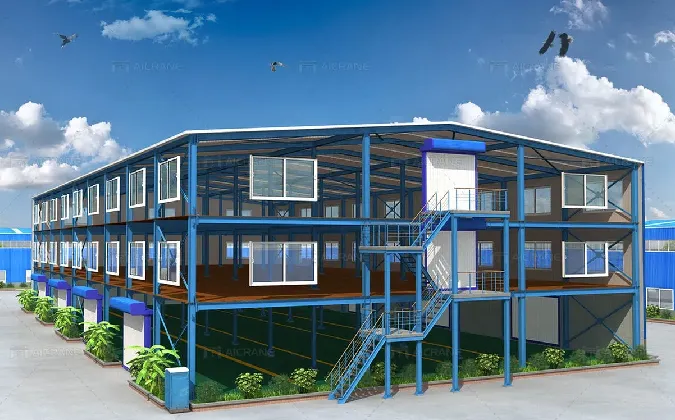
2. Multi-Story Factories
In contrast to single-story factories, multi-story factories make optimal use of vertical space. This type is particularly prevalent in urban areas where land is scarce and expensive. Multi-story designs allow for compact operations without sacrificing production capacity. These buildings often integrate elevators and conveyor systems to manage the movement of materials between floors.
Advantages - Efficient use of limited land space. - Potentially reduced transportation costs for raw materials and finished products. - Enhanced energy efficiency through centralized heating and cooling systems.
3. Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)
Flexible manufacturing systems are designed to adapt quickly to changes in production processes or product lines. These factory buildings are characterized by modular layouts, allowing for reconfiguration as business needs evolve. FMS is ideal for manufacturers producing a diverse range of products, as it enables quick changes in production without substantial downtime.
Advantages - Increased adaptability to market demands. - Reduced lead times for product changes. - Efficient use of resources and reduced waste.
factory building types

4. Lean Manufacturing Facilities
Lean manufacturing facilities focus on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity. These factories are designed around the principles of lean manufacturing, which prioritize continuous improvement and value creation. The layout typically emphasizes workflow optimization, with clearly defined pathways for materials and minimal interruptions.
Advantages - Higher efficiency and productivity rates. - Reduced operational costs through waste minimization. - Enhanced employee engagement by involving them in continuous improvement processes.
5. Green Manufacturing Buildings
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, green manufacturing buildings have emerged as a vital factory type. These structures incorporate environmentally friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies, aiming to reduce the overall carbon footprint of production processes. Features may include solar panels, rainwater harvesting systems, and natural ventilation.
Advantages - Reduced energy costs and improved overall sustainability. - Enhanced corporate image by demonstrating commitment to environmental responsibility. - Potential tax incentives or grants for green building initiatives.
6. Specialized Factories
Some manufacturing sectors require specialized factory buildings tailored to specific industry needs. For example, pharmaceutical production facilities must comply with stringent regulatory standards, necessitating specific design elements such as clean rooms and controlled environments. Similarly, food production factories must adhere to health and safety protocols, influencing their layout and building materials.
Advantages - Compliance with industry-specific regulations. - Enhanced safety and quality control measures. - Tailored environments to meet unique production needs.
Conclusion
The diversity of factory building types reflects the complexity and variability of modern manufacturing processes. Each factory type serves distinct operational needs, from single-story structures that facilitate straightforward logistics to specialized facilities designed for high-precision industries. As technology and market demands continue to evolve, the importance of innovative and efficient factory building designs will grow, ensuring that manufacturers can remain competitive in a dynamic global marketplace. Understanding the different factory types is crucial for effective planning, design, and operation within any industrial sector.
-
How Do Prefabricated Steel Structures Transform Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefabricated Metal Buildings Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefab Insulated Metal Buildings and Steel Structures Revolutionize Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Pre - Engineered Steel Structures Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Modular Construction with Prefabricated Metal Structures
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Industrial Infrastructure with Prefabricated Steel Solutions
NewsJul.14,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.