- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Aug . 29, 2024 22:52 Back to list
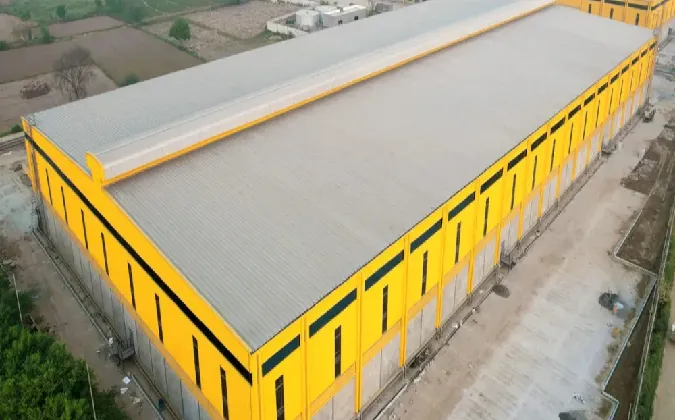
Foundations for Steel Frame Buildings
The foundation is a critical component in the construction of steel frame buildings, ensuring they possess the structural integrity necessary to support heavy loads and withstand various environmental factors. As a key element in architectural engineering, understanding the types of foundations, their design considerations, and construction techniques is essential for successful building projects.
Types of Foundations
There are primarily two types of foundations used for steel frame buildings shallow foundations and deep foundations. Shallow foundations are often used when the surface soil is stable and capable of supporting the loads from the building. Common forms include spread footings and slab-on-grade foundations, which distribute the building's weight over a larger area, mitigating settlement risks.
In scenarios where the soil depth or condition necessitates a more intricate solution, deep foundations become essential. Pile foundations and drilled shafts are typical types found in these situations. Piles are driven deep into the earth, reaching stable soil or bedrock, while drilled shafts are excavated and then filled with concrete to provide support at greater depths. These methods are particularly suitable for buildings located in areas with poor soil bearing capacity or where high seismic activity is a concern.
Design Considerations
Designing foundations for steel frame buildings involves evaluating several key factors. Firstly, the load-bearing capacity of the soil must be assessed to determine the type and size of the foundation required. Engineers perform geotechnical investigations to analyze soil characteristics, including density, cohesion, and type, which influence the foundation design.
foundations for steel frame buildings
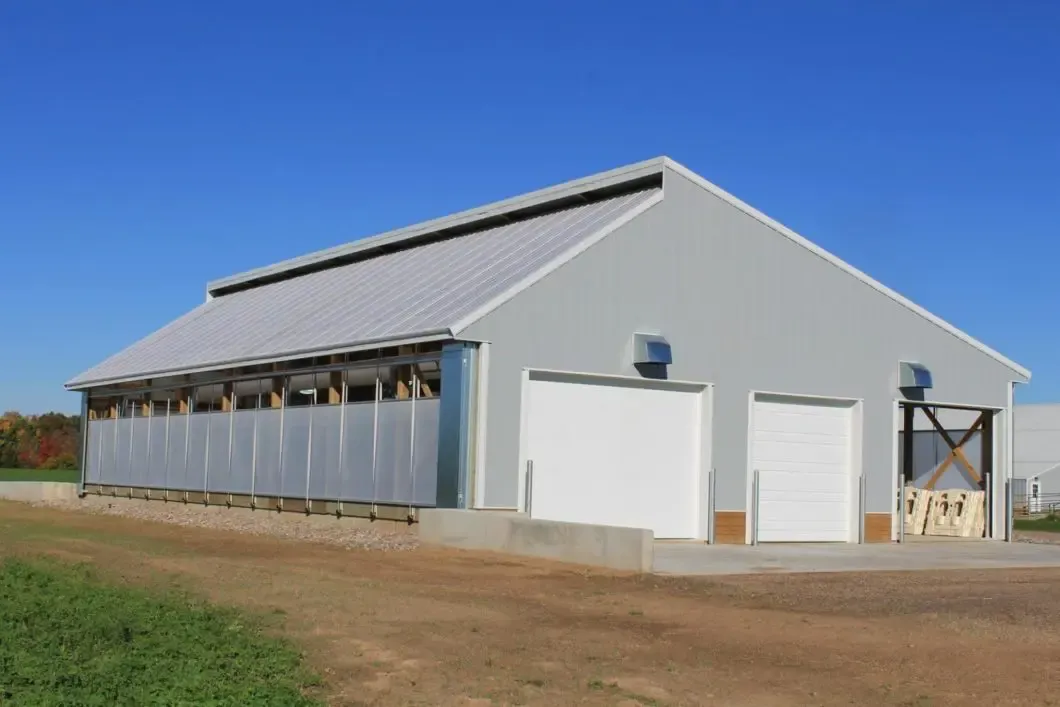

Secondly, the effects of environmental factors, such as seismic activity, flooding, or frost heave, need to be taken into account. For instance, in earthquake-prone regions, deep and flexible foundations might be employed to absorb shockwaves and prevent structural failure during tremors. Additionally, careful drainage design around the foundation is essential to prevent water accumulation, which can weaken soil and lead to foundation settlement.
Construction Techniques
The construction of foundations for steel frame buildings typically follows a systematic approach. After the design phase, the site is prepared through clearing and excavation. For shallow foundations, footings are dug and reinforced with rebar to enhance their strength. For deep foundations, piles are driven into the soil using pile driving equipment, or drilled into place with specialized drilling rigs.
Quality control during construction is vital to ensure that the foundations adhere to engineering specifications. This includes monitoring concrete curing, checking for proper alignment, and ensuring that all materials meet the required standards.
Conclusion
Foundations are the unsung heroes of steel frame buildings, playing a crucial role in the overall safety and longevity of the structure. By choosing the appropriate type of foundation based on soil conditions and environmental factors, and employing reliable construction techniques, engineers can ensure that steel frame buildings stand strong against the test of time. Properly designed and executed foundations not only support the weight of the superstructure but also provide resilience against natural forces, making them indispensable in modern architecture.
-
How Do Prefabricated Steel Structures Transform Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefabricated Metal Buildings Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefab Insulated Metal Buildings and Steel Structures Revolutionize Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Pre - Engineered Steel Structures Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Modular Construction with Prefabricated Metal Structures
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Industrial Infrastructure with Prefabricated Steel Solutions
NewsJul.14,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.