- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Nov . 05, 2024 03:23 Back to list
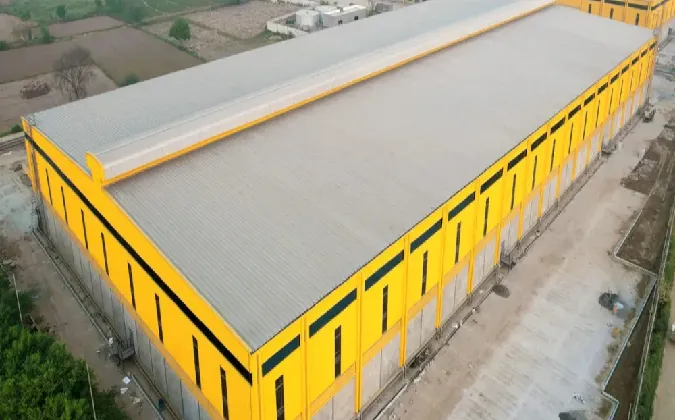
The Evolution of Industrial Buildings A Reflection on Functionality and Aesthetics
Industrial buildings have undergone significant transformation over the past century, evolving from mere functional spaces into remarkable architectural landmarks that often reflect the culture, technology, and economic climate of their time. These structures, once designed solely for the purpose of manufacturing and storage, have gained a new life, serving diversified roles in contemporary society while also showcasing creative design and sustainability.
Historically, industrial buildings were characterized by their robust structures made of steel and concrete, with little attention paid to aesthetics. The early 20th century saw factories that were primarily functional—large open spaces with high ceilings, wide doorways for machinery, and minimal external decoration. These buildings were designed to optimize production; their straightforwardness was a reflection of the industrial age’s emphasis on efficiency and productivity.
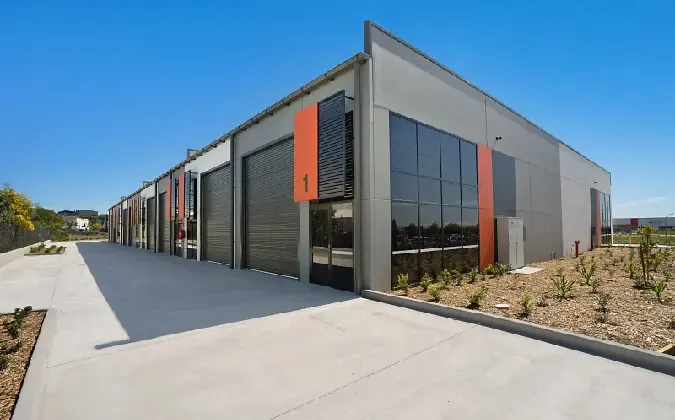
As the 21st century approached, however, the needs and expectations of industries began to evolve. The rise of the information age demanded more than just mere production capacity; it required adaptability, innovation, and a conducive work environment. This shift marked a departure from the traditional industrial building designs. Architects and urban planners started to rethink how these buildings could serve not just manufacturers but also local communities.
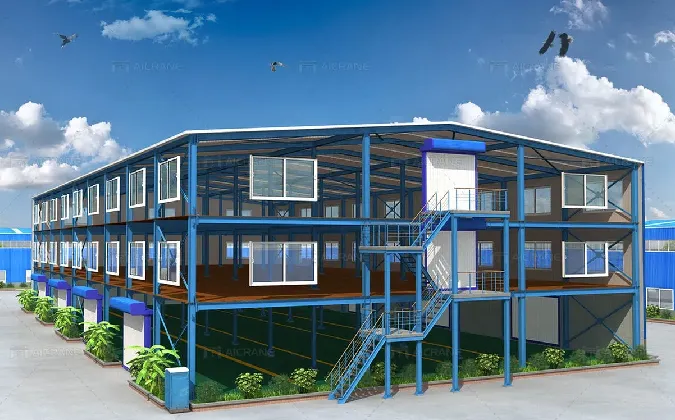
One of the pivotal changes in the design of industrial buildings has been the emphasis on sustainability. A growing awareness of environmental issues has led to innovative practices in building design. Modern industrial buildings are now constructed with eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient systems, and sustainable practices that minimize their carbon footprint. For instance, the integration of green roofs and solar panels has become commonplace. These practices not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also make the buildings more in tune with contemporary environmental standards and regulations.
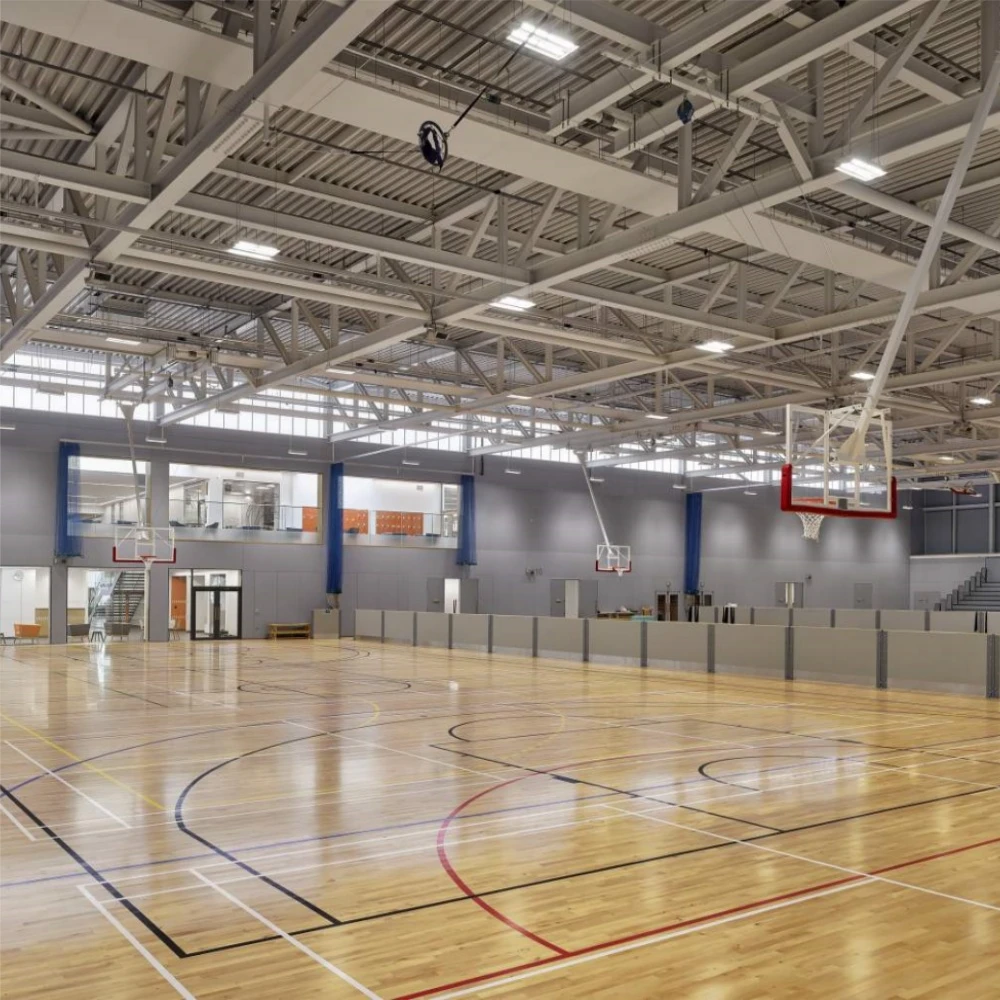
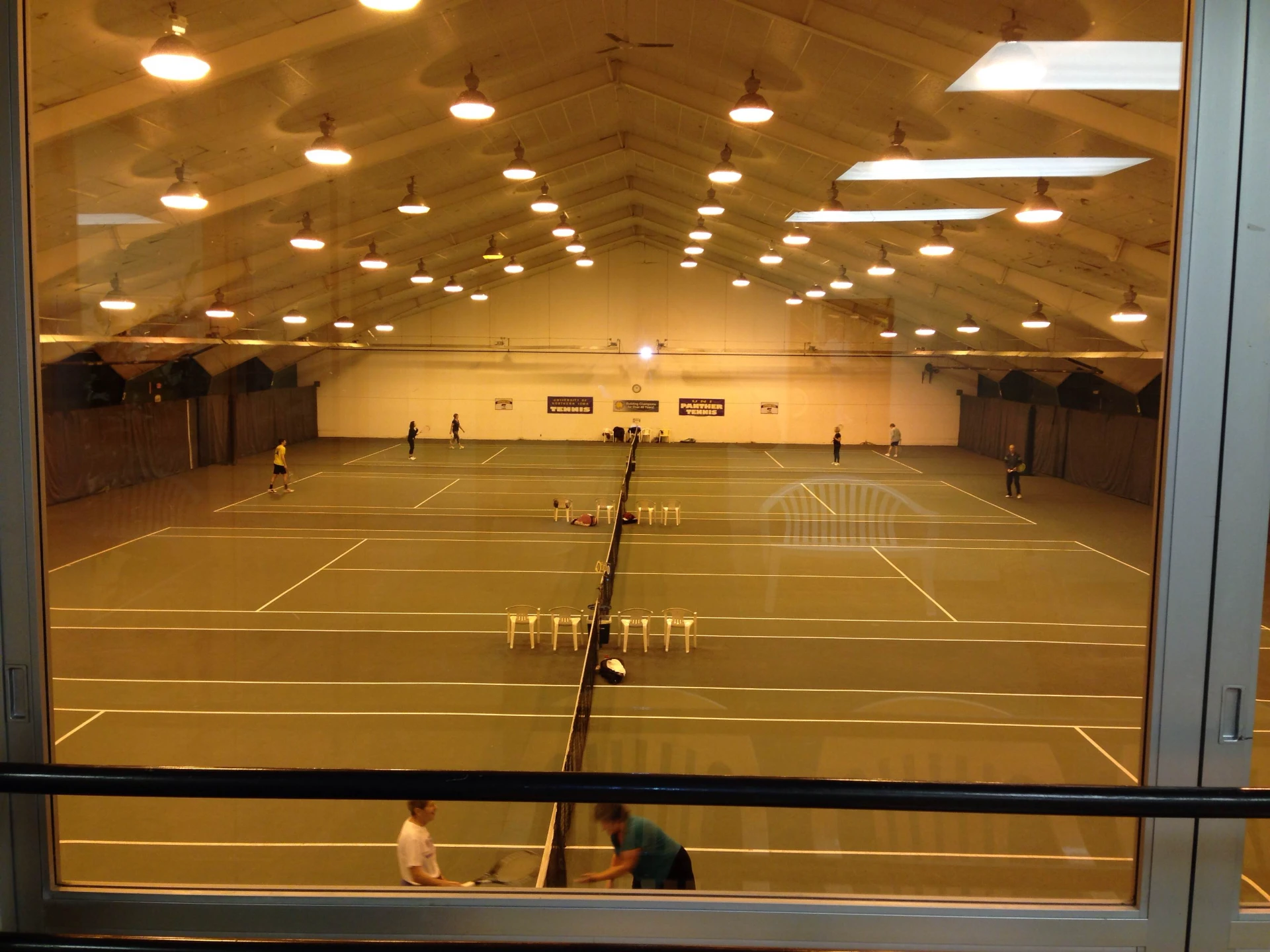
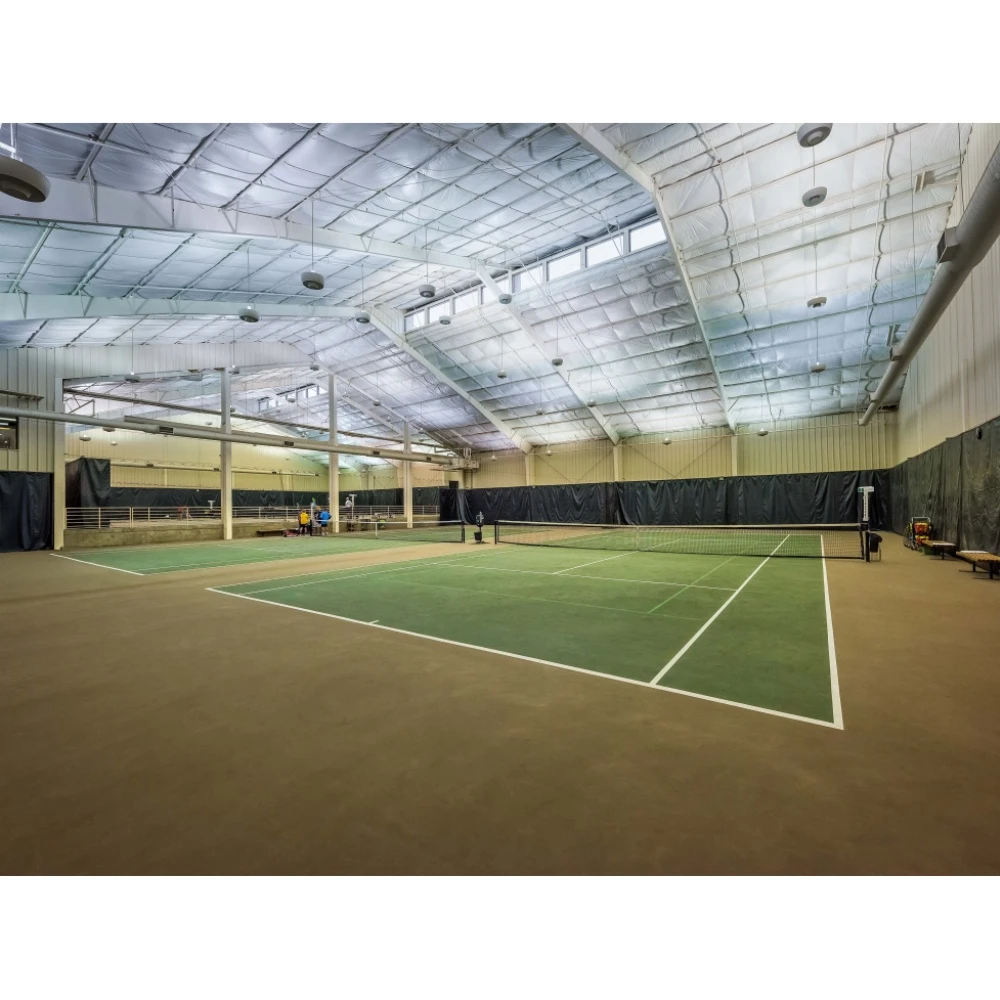
industrial building

Moreover, repurposing old industrial sites has become an exciting trend in urban development. Abandoned warehouses and factories are transformed into mixed-use spaces that combine residential, commercial, and cultural functionalities. Such projects often preserve the industrial character of the original structures while integrating modern design elements. The Tate Modern in London, a former power station converted into a renowned art museum, is a celebrated example of how industrial buildings can be revitalized and redefined. These conversions not only breathe new life into neighborhoods but also contribute to the preservation of architectural heritage.
The concept of adaptive reuse has expanded the narratives surrounding industrial buildings. No longer viewed as relics of the past, these structures are seen as valuable assets that can foster community engagement and economic growth. Their robust designs often lend themselves well to creative endeavors. Art studios, wedding venues, and coworking spaces have found a home in former factories, showcasing how flexibility in design can meet contemporary needs. This adaptability challenges the traditional notion of what industrial architecture represents, proving that the old can coexist harmoniously with the new.
The interaction between industrial buildings and their surroundings has also changed dramatically. Many modern developments focus on creating an inviting urban landscape that encourages public interaction. This includes green spaces, pedestrian pathways, and communal areas that provide opportunities for social gathering. The transformation of industrial sites into vibrant hubs promotes a sense of community, blending historical appreciation with modern functionality.
Additionally, as companies increasingly recognize the importance of employee well-being, the design of industrial workplaces has shifted to prioritize light, space, and aesthetics. Large windows, open floor plans, and thoughtful landscaping contribute to an environment that enhances creativity and productivity. This shift acknowledges that the physical space in which one works can significantly affect mental health and job satisfaction.
In conclusion, industrial buildings have come a long way from their utilitarian roots. They now play multifaceted roles that blend functionality with aesthetics, sustainability with history. As societies continue to change, so too will the way we view and utilize these structures. The industrial building of the future promises to be not only a space for production but also a catalyst for innovation, community engagement, and environmental stewardship. The evolution of these buildings is a testament to our ability to adapt and repurpose, turning the historical into the contemporary while honoring the past.
-
How Do Prefabricated Steel Structures Transform Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefabricated Metal Buildings Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Prefab Insulated Metal Buildings and Steel Structures Revolutionize Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
How Do Pre - Engineered Steel Structures Redefine Modern Construction?
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Modular Construction with Prefabricated Metal Structures
NewsJul.14,2025
-
Advancing Industrial Infrastructure with Prefabricated Steel Solutions
NewsJul.14,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.