- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Aug . 30, 2024 20:09 Back to list
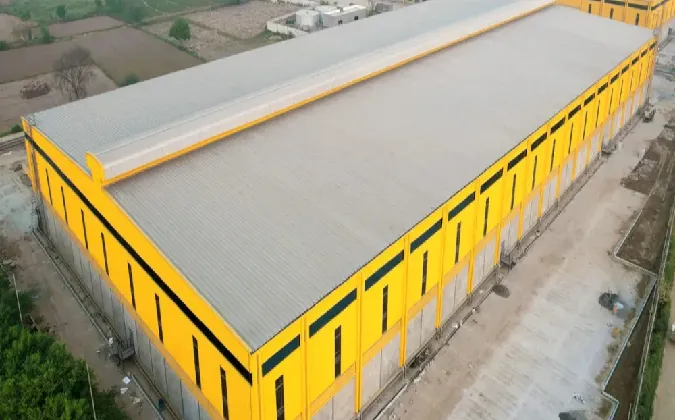
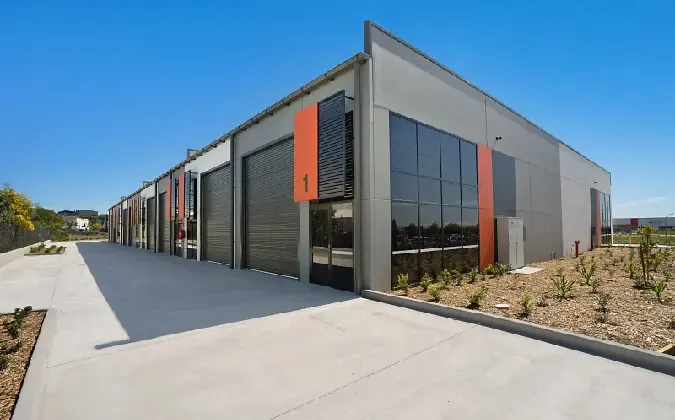
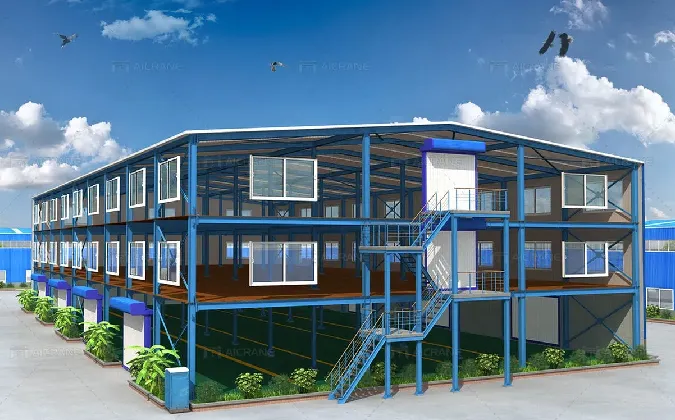
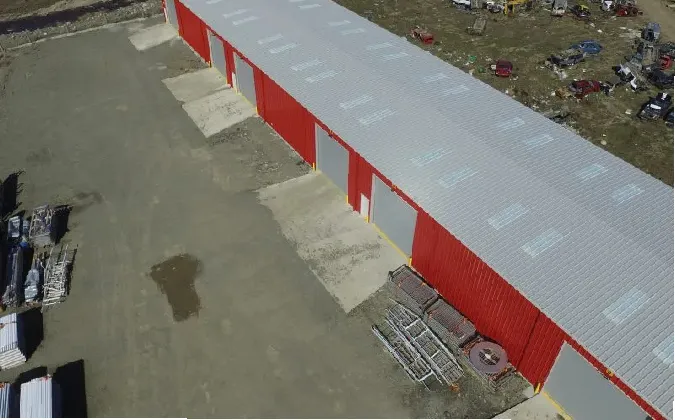
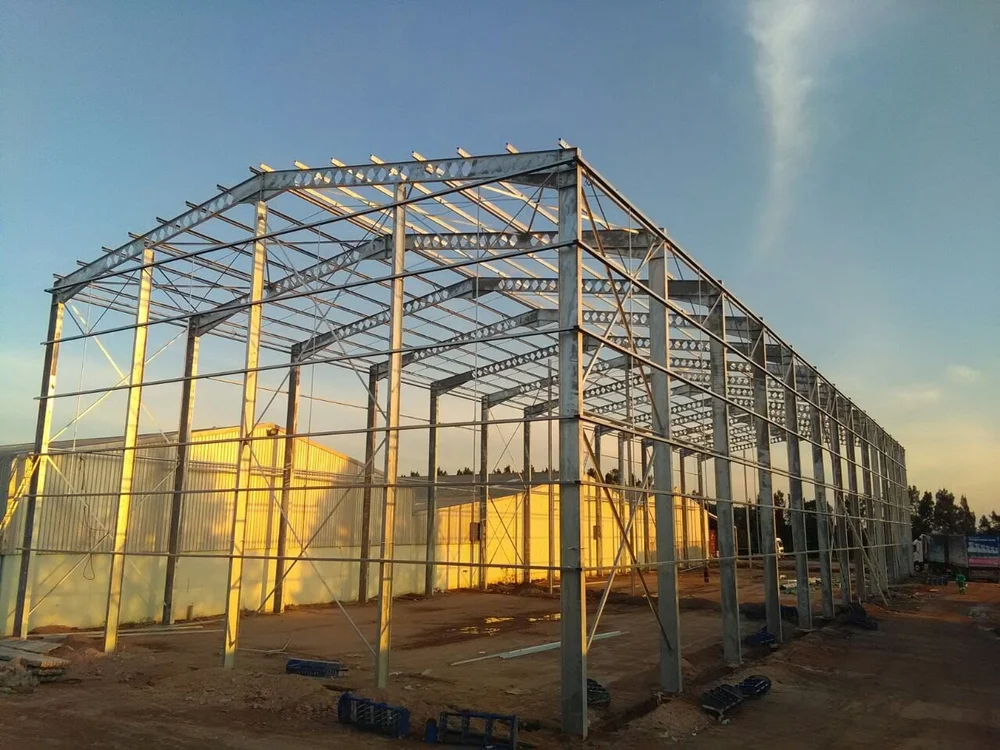
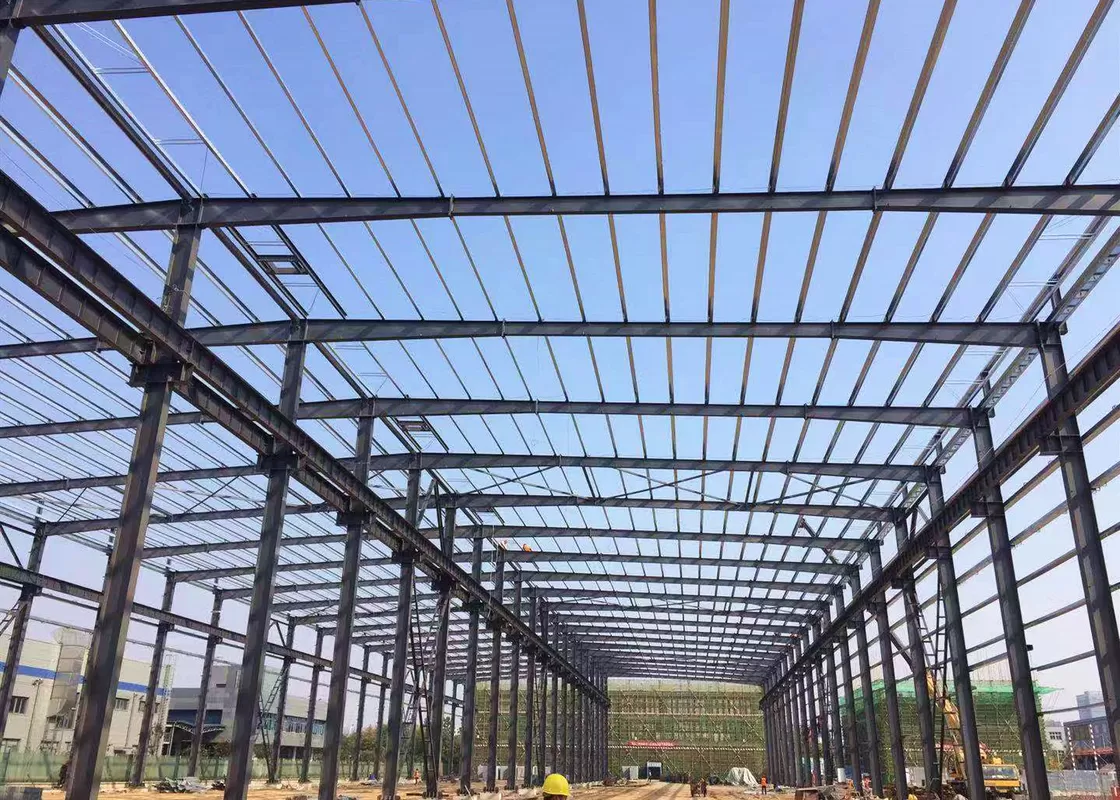
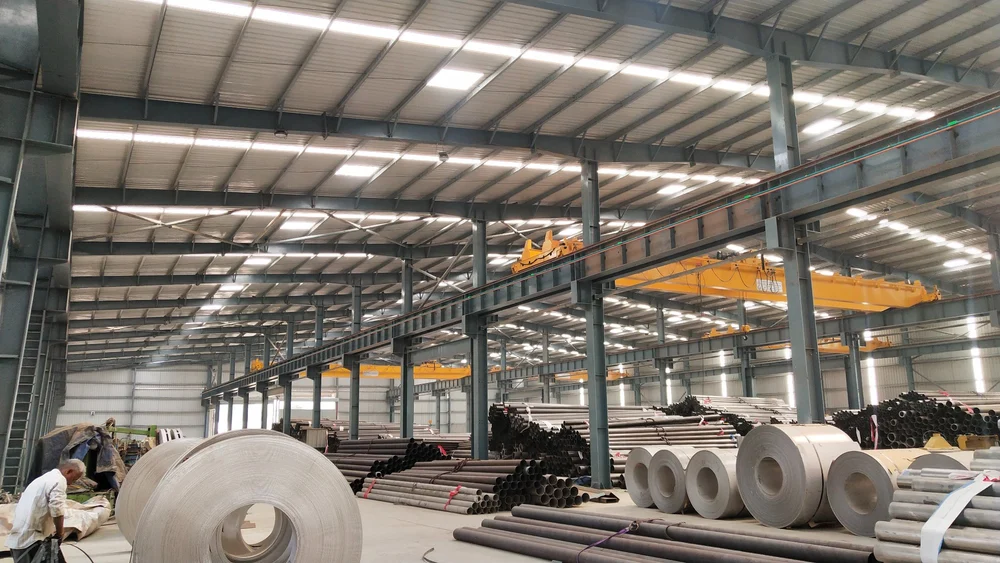
The Rise of Prefabricated Agricultural Buildings
In recent years, the agricultural sector has witnessed a significant transformation, largely due to advancements in technology and the growing need for efficiency. One of the most noteworthy developments has been the rise of prefabricated agricultural buildings. These structures, which are partially or fully manufactured in a factory setting before being transported to the site for assembly, have gained immense popularity among farmers and agricultural businesses. Their benefits are numerous, ranging from cost savings to versatility and sustainability.
One of the primary advantages of prefabricated agricultural buildings is cost-effectiveness. Traditional construction methods often come with high labor and material costs, which can strain the budgets of farmers, especially those operating on a smaller scale. Prefabricated buildings, however, can dramatically reduce these costs. Since they are constructed in a controlled environment, the materials can be used more efficiently, and construction time on-site is significantly reduced. Additionally, bulk purchasing of materials often results in lower prices, saving both money and time during the building process.
Another compelling reason for the popularity of prefabricated structures is their versatility. These buildings can serve a variety of agricultural purposes, including storage for equipment, livestock housing, or even refrigerated facilities for perishable goods. Their modular design allows for easy customization to meet specific needs, enabling farmers to adapt their buildings as their operations evolve. As the agricultural industry grows and diversifies, the flexibility of prefabricated buildings ensures that they can accommodate future changes without substantial renovations.
prefabricated agricultural buildings

Moreover, prefabricated agricultural buildings can be designed for sustainability. Many manufacturers are now focusing on eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs that can help farmers reduce their carbon footprint. For instance, using insulated panels can enhance temperature regulation within the buildings, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling. Additionally, some prefabricated structures can incorporate green technologies such as solar panels or rainwater collection systems, further promoting environmentally friendly practices in agriculture.
The construction speed of prefabricated buildings is another noteworthy benefit. In a world where time is of the essence and agricultural demands can change rapidly, the ability to erect a new structure in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods can be invaluable. This rapid deployment means that farmers can expand their operations quickly in response to market demands or unforeseen circumstances, such as natural disasters.
In conclusion, the trend of prefabricated agricultural buildings is reshaping the landscape of farming and agricultural business operations. With their cost-effectiveness, versatility, sustainability, and rapid construction times, these structures offer a practical solution to modern agricultural challenges. As the industry continues to evolve, it is likely that the adoption of prefabricated solutions will become even more widespread, enabling farmers to build efficiently while focusing on what truly matters producing quality food to feed the growing global population. The future of agriculture may very well rest on these innovative buildings, combining tradition with modernity for a sustainable tomorrow.
-
The Strength and Versatility of Industrial Metal Infrastructure
NewsAug.05,2025
-
The Landscape of Industrial Fabrication: Steel and Metal Factory Infrastructure
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Innovative Solutions for Industrial and Storage Spaces: Metal Building Garages and Workshops
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Evaluating Expenditures for Prefabricated Warehouse Structures
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Diverse Solutions for Industrial Spaces: Metal Workshop Buildings
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Analyzing Costs and Solutions in Industrial Steel Construction
NewsAug.05,2025
Products categories
Our Latest News
We have a professional design team and an excellent production and construction team.